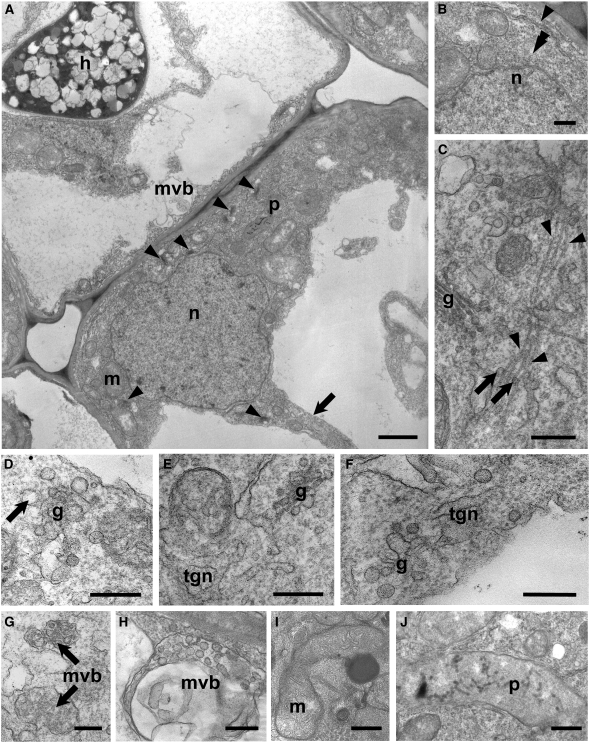
Figure 4.
TEM Imaging of PPA-Containing Inner Cortical Cells of D. carota.
(A) A typical PPA (extensive region of dense gray cytoplasm in the lower right-hand cell) associated with an enlarged nucleus (n) was positioned close to the junction with an adjacent inner cortical cell (above left) containing an AM hypha (h). Several Golgi stacks (arrowheads), mitochondria (m), and plastids (p) were visible within the broad cytoplasmic aggregation. Decondensed chromatin was present in the nucleus, and a narrow cytoplasmic bridge (arrow) was directed away from the approaching fungus. A smaller aggregation of cytoplasm and a multivesicular body (mvb) were visible in the adjacent colonized cell, ahead of the advancing hypha.
(B) to (J) High-magnification images of distinctive features of the PPA.
(B) Part of the nuclear envelope (double arrowhead) and an ER cisterna (arrowhead) in the vicinity of the nucleus (n).
(C) Vesicles (arrows) budding from a Golgi stack (g) and associated with bundled microtubules (arrowheads) oriented along the cytoplasmic bridge axis.
(D) Front view of a Golgi stack (g) with large, electron transparent budding vesicles (arrow).
(E) and (F) TGN membranes originating from the fusion of large vesicles budding from Golgi stacks.
(G) MVBs filled with small dense vesicles.
(H) Large multivesicular body, containing large-size electron-transparent vesicles.
(I) Dividing mitochondrion (m), rich in cristae and associated with an electron-dense body.
(J) Chromoplast-like plastid (p) devoid of starch granules, containing several electron-dense membranes and globules.
Bars = 2 μm in (A), 0.5 μm in (B) and (D), and 0.25 μm in (C) and (E) to (J).