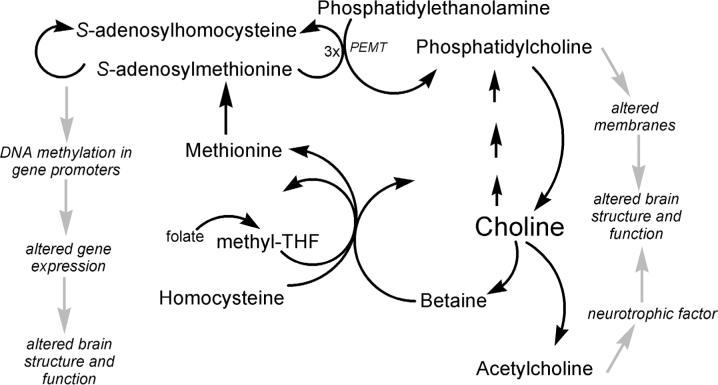
Figure 1.
Metabolism of choline and possible mechanisms for effects on brain structure and function. Choline is acetylated to form acetylcholine, which is a trophic factor for brain. Choline is phosphorylated and then used to form membranes that are required for brain function. Finally, choline is a methyl-group donor that can influence DNA methylation and gene expression, which can, in turn, alter brain structure and function. Methyl-THF = methyltetrahydrofolate.