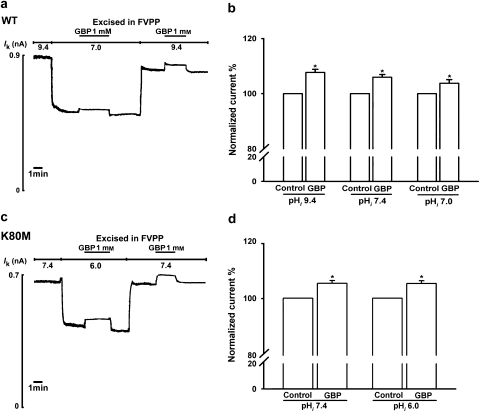
Figure 2.
Gabapentin (GBP; 1-(aminomethyl) cyclohexaneacetic acid) activates renal outer medullary potassium (ROMK1) activity in an intracellular pH (pHi)-independent manner. (a) Representative current trace from giant inside-out patches showing that 1 mM gabapentin enhances wild-type ROMK1 channel activity at pHi 7.0 and pHi 9.4. (b) Activity of wild-type ROMK1 channels in the presence of 1 mM gabapentin expressed as a percentage of the corresponding control levels at pHi 9.4, 7.4 or 7.0 (n=6 for each group). *Indicates P<0.05 by Student's t-test compared with the corresponding pHi control. (c) Gabapentin (1 mM) activates the K80M mutant channel at pHi 7.4 and 6.0. The experimental paradigm was the same as that in panel a. (d) Activation of K80M channels by 1 mM gabapentin at pHi 7.4 and 6.0 (n=5 for each group). *Indicates P<0.05 by Student's t-test compared with the corresponding pHi for control.