Abstract
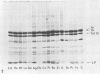
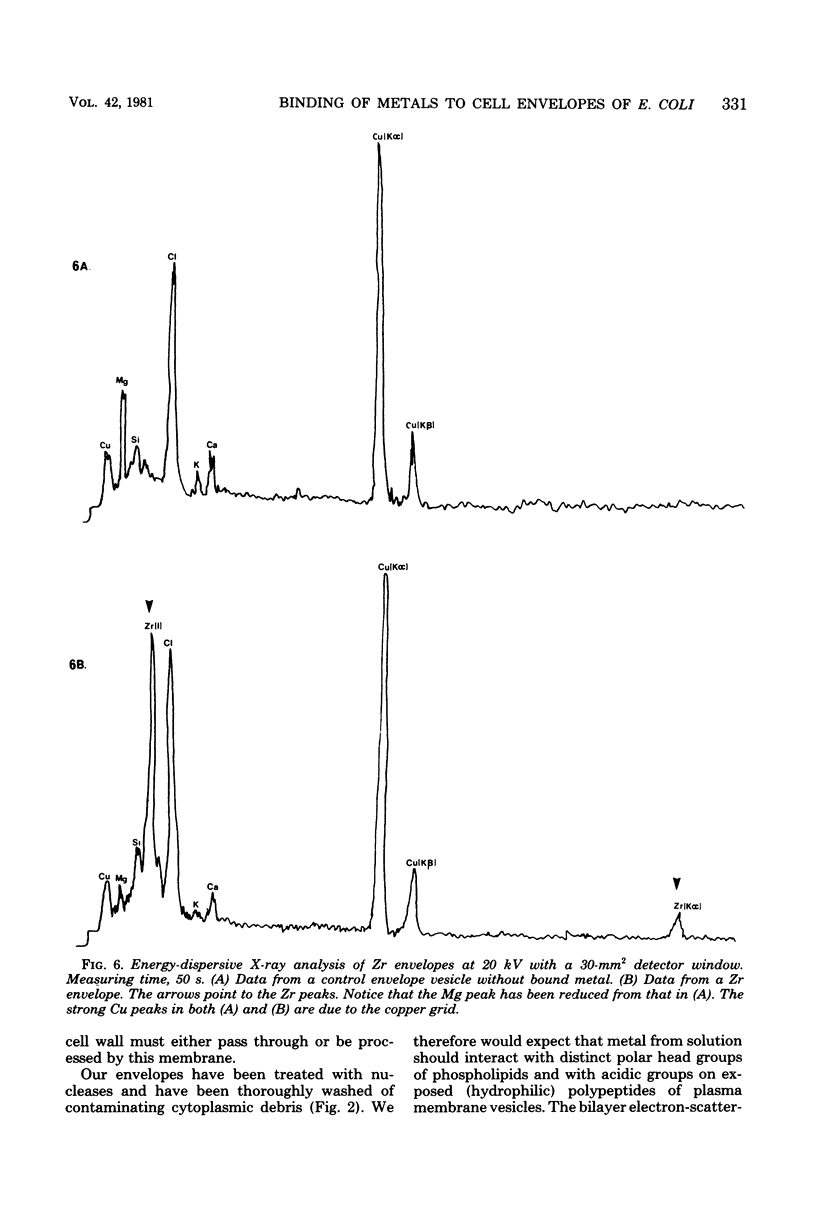
As representative of gram-negative bacteria, the isolated and purified envelopes of an Escherichia coli K-12 strain were used to determine metal-binding capacity. The envelopes were suspended in 5 mM metal solutions for 10 min and 23 degrees C, separated and washed by centrifugation, and analyzed for metal by either atomic absorption or X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. Of 32 metals tested, large amounts (> 0.9 mumol/mg [dry weight]) of Hf and Os, intermediate amounts (0.1 to 0.4 mumol/mg [dry weight]) of Pb, Zn, Zr, Fe III, Mn, Mo, Mg, Co, and Ce IV, and small amounts (< 0.1 mumol/mg [dry weight]) of Na, K, Rb, Ca, Sr, Cu, Sc, La, Pr, Sm, U, Fe II, Ru, Ni, Hg, Pt, Pd, Au, and In were detected Li and V were not bound to the envelopes. Electron microscopy of unstained, thin-sectioned material provided an electron-scattering profile for localizing the bound metal within the envelope. Energy-dispersive X-ray analysis of thin sections detected all metals in single envelope vesicles. These data suggest that most metal deposition occurred at the polar head group regions of the constituent membranes or along the peptidoglycan layer. No leaching of envelope components was detected by monitoring radioactive probes within the lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan layers during metal uptake experiments, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of proteins from metal-loaded envelopes, or protein and carbohydrate determinations on the wash fluids. These results suggest that membrane integrity was not disturbed under these ionic conditions.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arancia G., Belli S., Donelli G., Trovalusci P. Ultrastructural changes in Escherichia coli grown in divalent cation-deficient medium. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jul;119(1):155–164. doi: 10.1099/00221287-119-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald F. S., DeVoe I. W. Iron in Neisseria meningitidis: minimum requirements, effects of limitation, and characteristics of uptake. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):35–48. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.35-48.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswell J. E., Haydon A. H., Turner H. R., Dawkins C. A., Arceneaux J. E. Specificity of siderophore receptors in membrane vesicles of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):173–180. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.173-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barghoorn E. S., Tyler S. A. Microorganisms from the Gunflint Chert: These structurally preserved Precambrian fossils from Ontario are the most ancient organisms known. Science. 1965 Feb 5;147(3658):563–575. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3658.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Sites of metal deposition in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):876–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.876-887.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Uptake and retention of metals by cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1502–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1502-1518.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J. The response of cell walls of Bacillus subtilis to metals and to electron-microscopic stains. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Feb;24(2):89–104. doi: 10.1139/m78-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
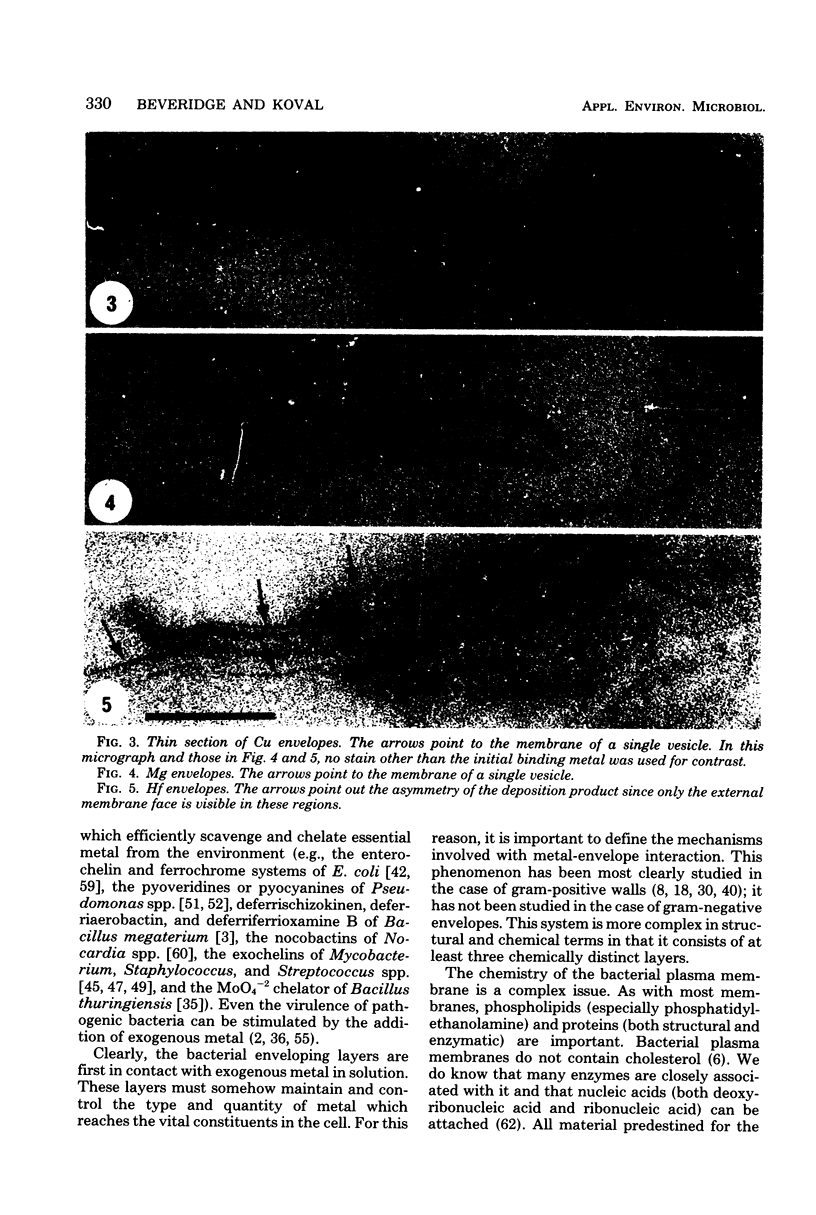
- Beveridge T. J. Ultrastructure, chemistry, and function of the bacterial wall. Int Rev Cytol. 1981;72:229–317. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen E. L., Cox H. A., Mercer W. B., Natale L. A. Passive Electrical Properties of Microorganisms: I. Conductivity of Escherichia coli and Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biophys J. 1965 May;5(3):289–300. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(65)86717-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen E. L. Passive electrical properties of microorganisms. II. Resistance of the bacterial membrane. Biophys J. 1967 Sep;7(5):493–503. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86600-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutinelli C., Galdiero F. Capacità legante ioni del cell-wall di Staphylococcus aureus. Riv Biol. 1967 Apr-Jun;60(2):285–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Matthews T. H., Streips U. N. Chemical basis for selectivity of metal ions by the Bacillus subtilis cell wall. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):471–480. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.471-480.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyar M. T., Ordal E. J. Electrokinetic Studies on Bacterial Surfaces: I. Effects of Surface-active Agents on Electrophoretic Mobilities of Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1946 Feb;51(2):149–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglinton G., Scott P. M., Belsky T., Burlingame A. L., Calvin M. Hydrocarbons of Biological Origin from a One-Billion-Year-Old Sediment. Science. 1964 Jul 17;145(3629):263–264. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3629.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einolf C. W., Jr, Carstensen E. L. Bacterial conductivity in the determination of surface charge by microelectrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 28;148(2):506–516. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einolf C. W., Jr, Carstensen E. L. Passive electrical properties of microorganisms. IV. Studies of the protoplasts of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biophys J. 1969 Apr;9(4):634–643. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86408-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funahara Y., Nikaido H. Asymmetric localization of lipopolysaccharides on the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1463–1465. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1463-1465.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdiero F., Lembo M., Tufano M. A. Affinity of various cations for Staphylococcus aureus cell-wall. Experientia. 1968 Jan 15;24(1):34–36. doi: 10.1007/BF02136776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenslate J. Manganese and biotic debris associations in some deep-sea sediments. Science. 1974 Nov 8;186(4163):529–531. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4163.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDEN V. P., HARRIS J. O. The isoelectric point of bacterial cells. J Bacteriol. 1953 Feb;65(2):198–202. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.2.198-202.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heptinstall S., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. Teichoic acids and membrane function in bacteria. Nature. 1970 Feb 7;225(5232):519–521. doi: 10.1038/225519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin R. T., Chatterjee A. K., Sanderson K. E., Costerton J. W. Comparison of the cell envelope structure of a lipopolysaccharide-defective (heptose-deficient) strain and a smooth strain of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):930–941. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.930-941.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketchum P. A., Owens M. S. Production of molybdenum-coordinating compound by Bacillus thuringiensis. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):412–417. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.412-417.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung F. C., Raymond J., Glaser D. A. Metal ion content of Escherichia coli versus cell age. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1089–1095. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1089-1095.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. A., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. The interaction of magnesium ions with teichoic acid. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):519–524. doi: 10.1042/bj1490519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L., Shovlin V. K., Mergenhagen S. E. Physical, chemical, and immunological properties of lipopolysaccharide released from Escherichia coli by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6384–6391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J., Neilands J. B. Mechanisms of siderophore iron transport in enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):823–830. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.823-830.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macham L. P., Ratledge C. A new group of water-soluble iron-binding compounds from Mycobacteria: the exochelins. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Aug;89(2):379–382. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-2-379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelis J. H., den Daas-Slagt H. J., Hoogkamp-Korstanje J. A. Iron requirement and chelator production of staphylococci, Streptococcus faecalis and enterobacteriaceae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1978;44(3-4):257–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00394304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis R. E., Mayzel K., Carstensen E. L. Cation exchange in cell walls of gram-positive bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jul;22(7):975–982. doi: 10.1139/m76-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullough W. G., Merkal R. S. Iron-chelating compound from Mycobacterium avium. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):15–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.15-20.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQUILLEN K. The bacterial surface. I. Effect of cetyl-trimethyl-ammonium bromide on the electrophoretic mobility of certain gram-positive bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jun;5(3/4):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90192-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley G. A., Card G. L., Koostra W. L. Effect of calcium and anaerobiosis on the thermostability of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Apr;22(4):468–474. doi: 10.1139/m76-073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osada Y., Une T., Ikeuchi T., Ogawa H. Divalent cation stimulation of the cell infectivity of Shigella flexneri 2a. Jpn J Microbiol. 1975 Apr;19(2):163–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1975.tb00863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Wu H. C. Proteins of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:369–422. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Reeves P. Iron uptake in colicin B-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1052–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1052-1062.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratledge C., Patel P. V. Isolation, properties and taxonomic relevance of lipid-soluble, iron-binding compounds (the nocobactins) from Nocardia. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Mar;93(1):141–152. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-1-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. W., Gilleland H. E., Jr, Eagon R. G. Characterization of a protein-lipopolysaccharide complex released from cell walls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jul;15(7):743–748. doi: 10.1139/m69-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R., Owen P. Bacterial membrane structure. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:451–482. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schott H., Young C. Y. Electrokinetic studies of bacteria. 3. Effect of polyvalent metal ions on electrophoretic mobility and growth of Streptococcus faecalis. J Pharm Sci. 1973 Nov;62(11):1797–1801. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600621112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John A. C., Goldberg A. L. Effects of starvation for potassium and other inorganic ions on protein degradation and ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1223–1233. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1223-1233.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEBE I. EXTENT OF CROSS LINKAGE IN THE MUREIN SACCULUS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI B CELL WALL. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 1;101:124–126. doi: 10.1016/0926-6534(65)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting-Beall H. P. Interactions of uranyl ions with lipid bilayer membranes. J Microsc. 1980 Feb;118(2):221–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1980.tb00264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Träuble H., Eibl H. Electrostatic effects on lipid phase transitions: membrane structure and ionic environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):214–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Hasan S. M., Raven J. Glutamate transport driven by an electrochemical gradient of sodium ions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Sep;131(3):848–853. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.3.848-853.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voll M. J., Leive L. Release of lipopolysaccharide in Escherichia coli resistant to the permeability increase induced by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):1108–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M. Effects of magnesium deficiency on ribosomal structure and function in certain Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 24;222(2):416–427. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. L. Site-specific membrane particle arrays in magnesium-depleted Escherichia coli. J Cell Biol. 1977 May;73(2):505–519. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]