Abstract
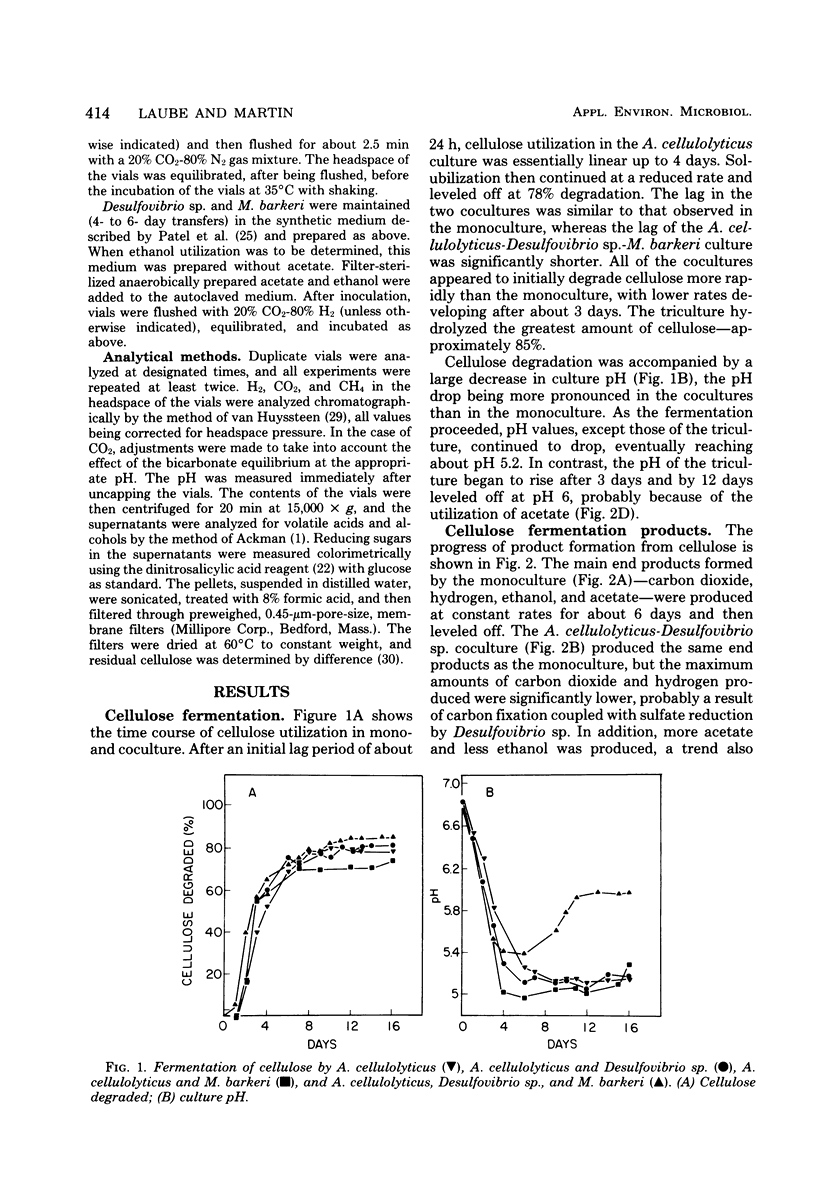
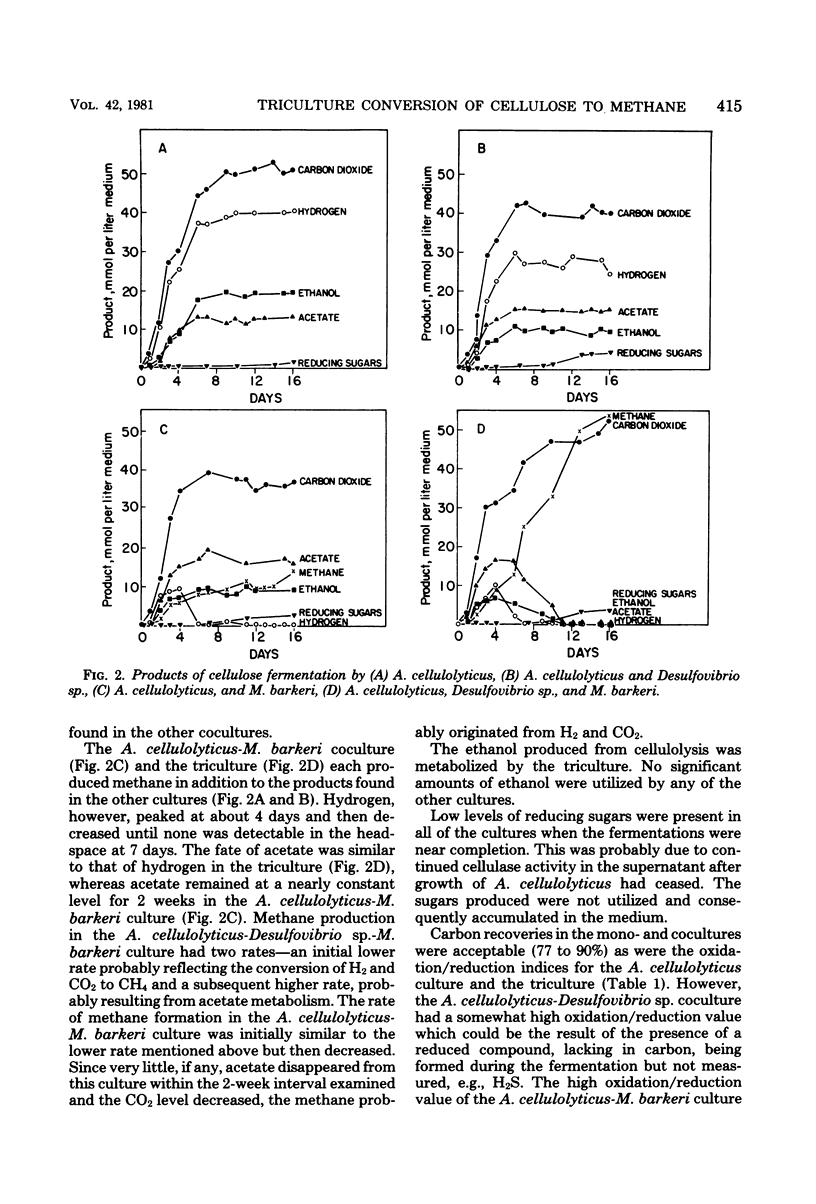
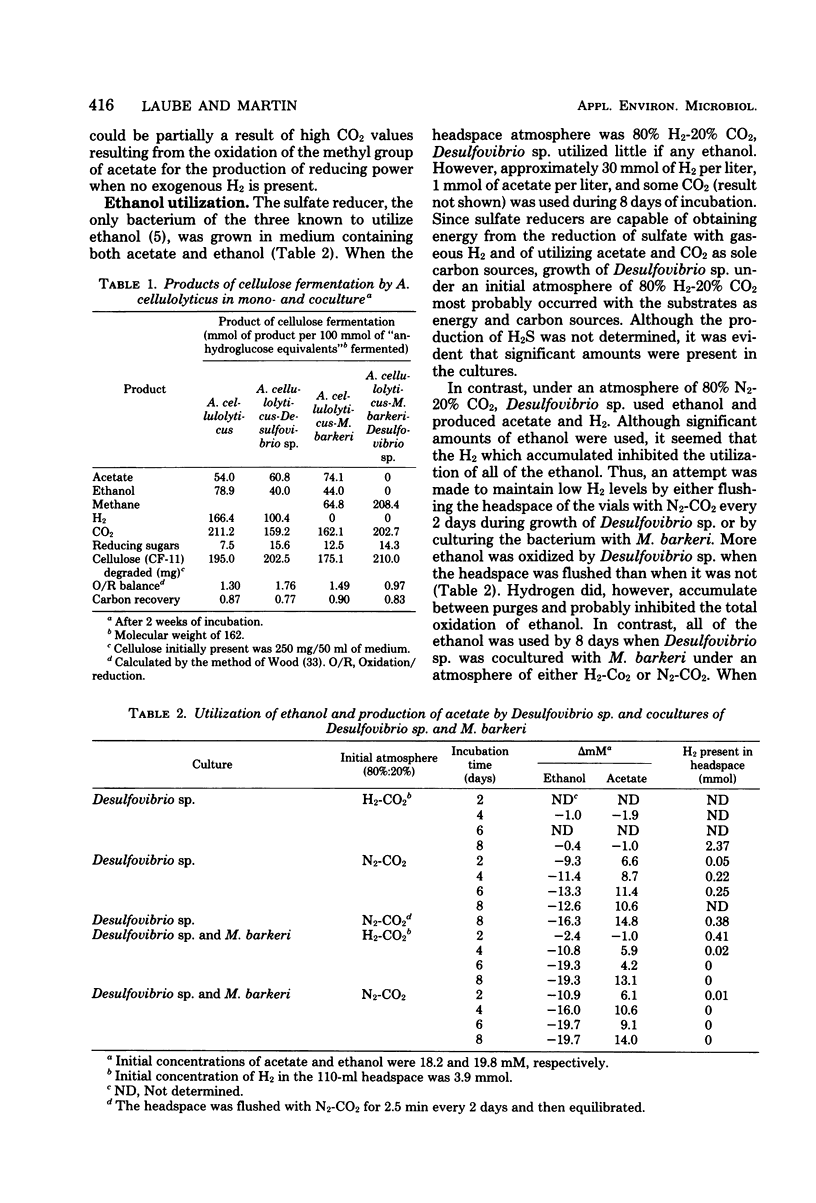
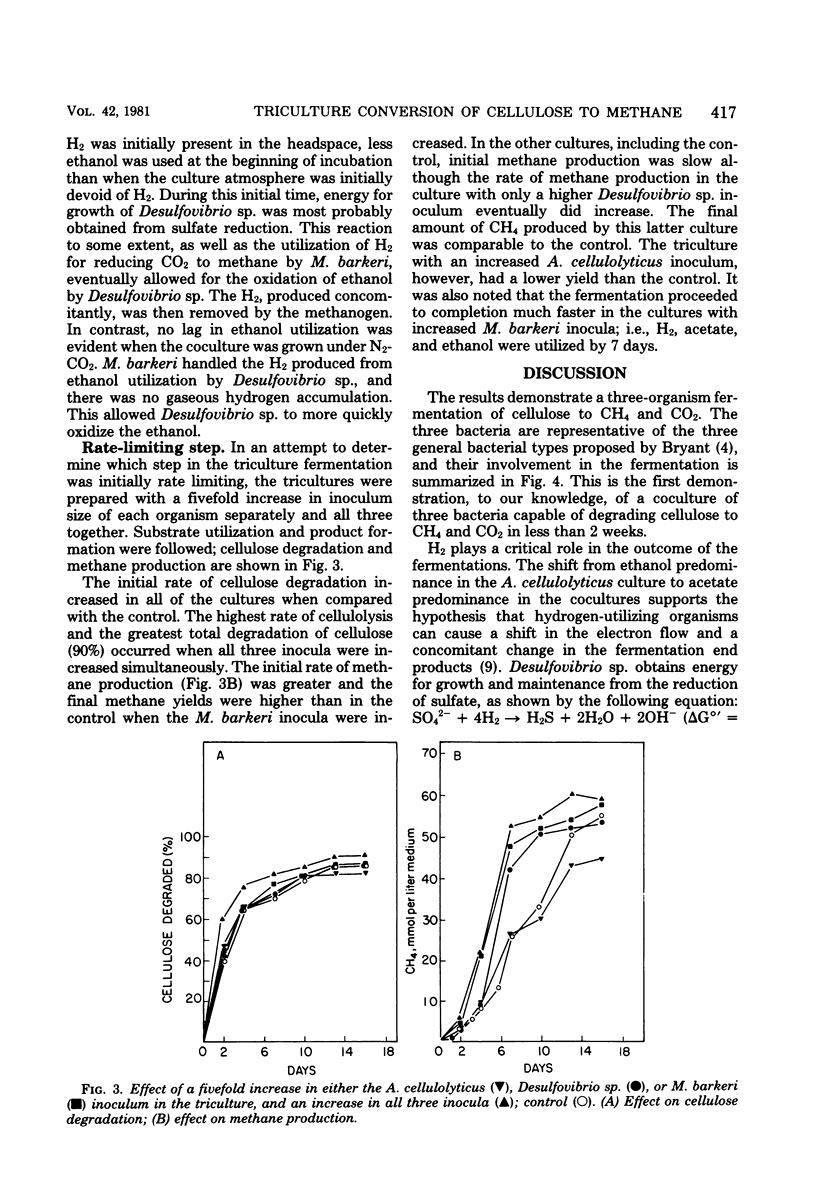
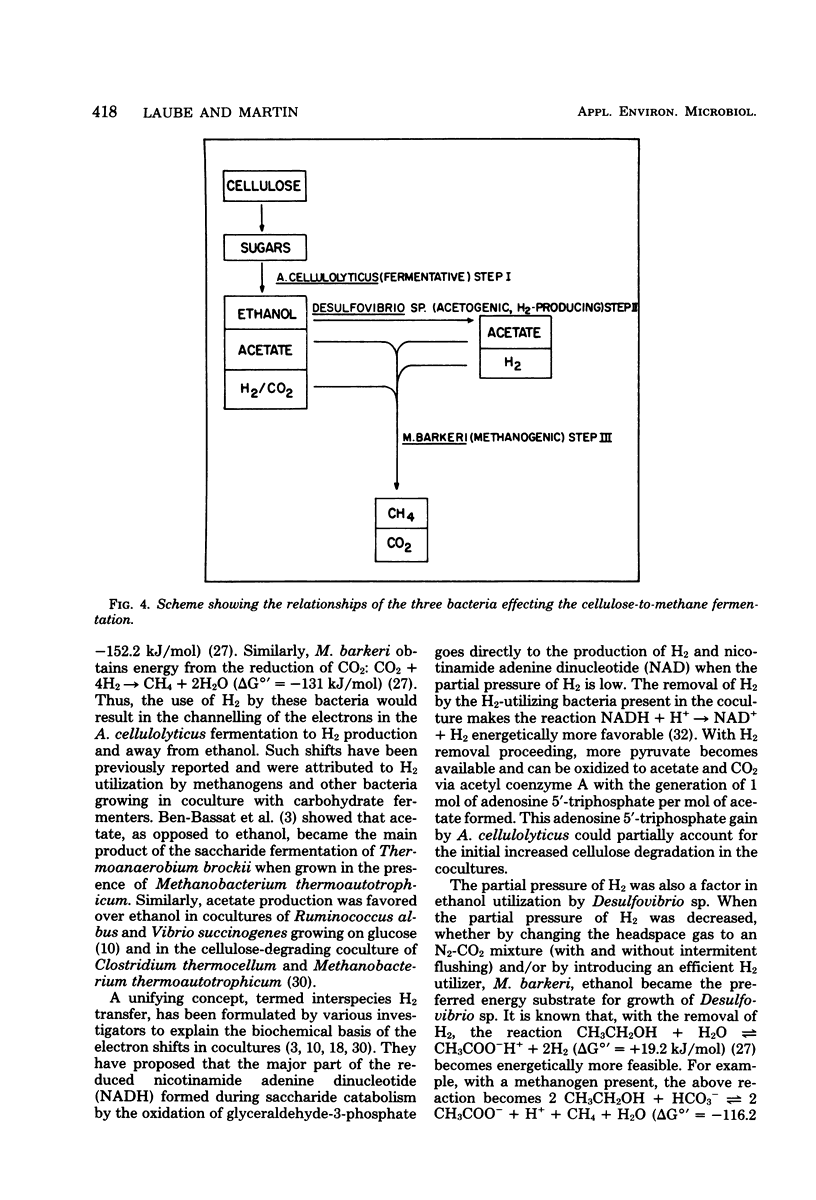
The fermentation of cellulose by monocultures of Acetivibrio cellulolyticus and cocultures of A. cellulolyticus-Methanosarcina barkeri, A. cellulolyticus-Desulfovibrio sp., and A. cellulolyticus-M. barkeri-Desulfovibrio sp. was studied. The monoculture produced ethanol, acetate, H2, and CO2. More acetate and less ethanol was formed by the cocultures than by the monoculture. Acetate was utilized by M. barkeri in coculture with A. cellulolyticus after a lag period, whereas ethanol was metabolized by the sulfate reducer only under conditions of low H2 partial pressure, i.e., when cocultured with A. celluloyticus-M. barkeri or when grown together with the methanogen. Only the three-component culture carried out the rapid conversion of cellulose to CO2 and methane. Furthermore, this culture hydrolyzed the most cellulose—85% of that initially present. This amount was increased to 90% by increasing the population of M. barkeri in the triculture. Methane production was also increased, and a quicker fermentation rate was achieved.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackman R. G. Porous polymer bead packings and formic acid vapor in the GLC of volatile free fatty acids. J Chromatogr Sci. 1972 Sep;10(9):560–565. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/10.9.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badziong W., Thauer R. K., Zeikus J. G. Isolation and characterization of Desulfovibrio growing on hydrogen plus sulfate as the sole energy source. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Jan 23;116(1):41–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00408732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., Campbell L. L., Reddy C. A., Crabill M. R. Growth of desulfovibrio in lactate or ethanol media low in sulfate in association with H2-utilizing methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1162–1169. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1162-1169.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., Wolin E. A., Wolin M. J., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacillus omelianskii, a symbiotic association of two species of bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):20–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00406313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iannotti E. L., Kafkewitz D., Wolin M. J., Bryant M. P. Glucose fermentation products in Ruminococcus albus grown in continuous culture with Vibrio succinogenes: changes caused by interspecies transfer of H 2 . J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1231–1240. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1231-1240.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. W. Anaerobic degradation of cellulose by mixed culture. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Dec;23(12):1700–1705. doi: 10.1139/m77-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. W., Trottier T. M. Effect of sulfur-containing compounds on anaerobic degradation of cellulose to methane by mixed cultures obtained from sewage sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1027–1034. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1027-1034.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham M. J., Wolin M. J. Fermentation of cellulose by Ruminococcus flavefaciens in the presence and absence of Methanobacterium ruminantium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Sep;34(3):297–301. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.3.297-301.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mah R. A., Smith M. R., Baresi L. Studies on an acetate-fermenting strain of Methanosarcina. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1174–1184. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1174-1184.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountfort D. O., Asher R. A. Effect of inorganic sulfide on the growth and metabolism of Methanosarcina barkeri strain DM. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Apr;37(4):670–675. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.4.670-675.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel G. B., Roth L. A., van den Berg L., Clark D. S. Characterization of a strain of Methanospirillum hungatti. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Sep;22(9):1404–1410. doi: 10.1139/m76-208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Jungermann K., Decker K. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):100–180. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.100-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer P. J., Zeikus J. G. Fermentation of cellulose and cellobiose by Clostridium thermocellum in the absence of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):289–297. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.289-297.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter J., Wolfe R. S. Complete degradation of carbohydrate to carbon dioxide and methane by syntrophic cultures of Acetobacterium woodii and Methanosarcina barkeri. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Apr;121(1):97–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00409211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin M. J. Metabolic interactions among intestinal microorganisms. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Nov;27(11):1320–1328. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.11.1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


