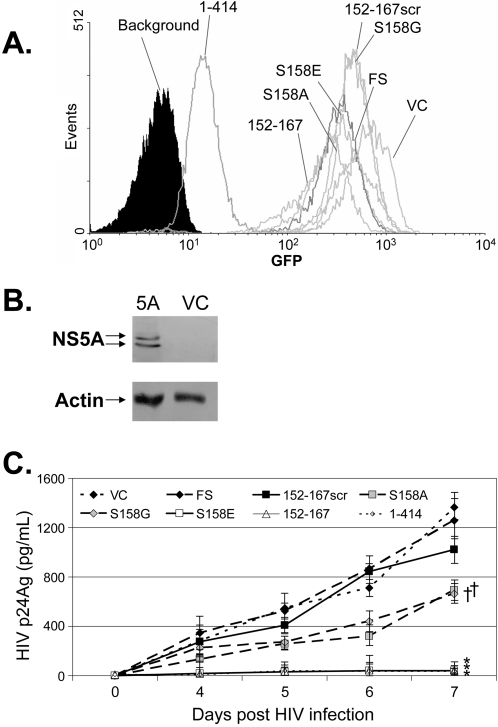
Figure 3. Mutational analysis of GBV-C 152–167 NS5A peptide.
Clonal cell lines stably transfected with NS5A peptides were selected by hygromycin resistance and examined for GFP expression (A). Cells expressed the full length NS5A protein (amino acids 1–414), an NS5A 16 amino acid protein (152–167), the same 16 amino acids scrambled (152–167scr), or peptides in which the serine (position 158) was replaced with alanine (S158A), glycine (S158G) or glutamic acid (S158E). VC = vector control cells and FS = frame-shift control cells. Background represents the background fluorescence of parental Jurkat cells. Panel B demonstrates two immunoreactive NS5A proteins in cells expressing 1–414 (5A) but not in the vector control (VC) cells. Actin loading controls are shown. HIV replication was significantly decreased in Jurkat cell lines expressing full-length NS5A (1–414), the 152–167 peptide, and the S158E mutant (*) compared to all other cell lines on days 5, 6, and 7 days post-infection (panel C). The S158A and S158G cell lines had significantly less HIV replication than FS and VC (†; P = 0.041 on day 7), but significantly more HIV replication than the 1–414, 152–167, and S158E cells (†; P<0.02 for all, day 7).