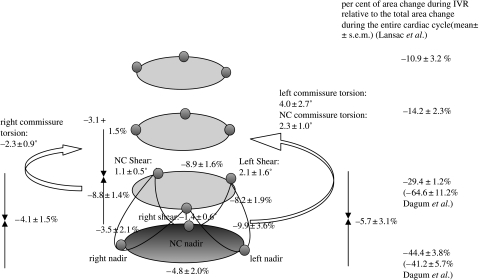
Figure 9.
Aortic root deformations during IVR. Data from Dagum et al. expressed as group mean±s.d. per cent change of deformation (longitudinal, circumferential, shear and torsion) during IVR unless specified otherwise. During IVR, the aortic root underwent further circumferential contraction (Dagum et al. 1999). The greatest circumferential contraction of the annulus occurs at the left base and the least at the NC base. In contrast to asymmetric annular circumferential contraction, the left, right and NC sinuses at the commissures contracted symmetrically. In addition, during IVR, the aortic root sheared and underwent torsional deformation and longitudinal compression. Longitudinal compression of the aortic root was symmetric among the left, right and NC regions of the aortic root (Dagum et al. 1999). The per cent area change relative to the total change over the entire cardiac cycle of the base and commissures during IVR was −41±6 and −65±11%, respectively (Dagum et al. 1999). Lansac et al. (2002) observed the following per cent area change during IVR at different levels of the aortic root: base, −44±4%; commissures, −29±1%; STJ, −14±2%; ascending aorta, −10.9±3.2%.