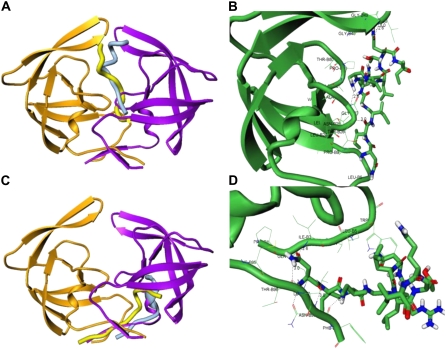
FIGURE 3.
Structural characterization of the peptide-binding modes in complexes with the HIV-1 monomers. (A) The thermodynamically stable conformation of the rigid p-S8 peptide (in light blue) in the complex with the HIV-1 monomer (orange ribbons). The predicted folded conformation of the flexible p-S8 peptide (in yellow) binds to the HIV-1 PR monomer (green ribbons) in the same binding mode as determined in simulations with the rigid peptide. The bound peptide conformations overlayed with the conformation of the second HIV-1 PR monomer (violet ribbons) reveals structural mimicry with the fireman's-grip hydrogen-bond network present in the active dimer. (B) A closeup of the binding interface and specific interactions formed by the folded peptide in the folding mode of inhibition. (C) An alternative binding mode of the rigid p-S8 peptide (in light blue) and folded conformation of the flexible p-S8 peptide (in yellow) in the complex with the HIV-1 monomer (orange ribbons). The bound peptide conformations overlayed with the conformation of the second HIV-1 PR monomer (violet ribbons) mimics another important region of the dimerization interface. (D) A closeup of the binding interface and specific interactions formed by the folded peptide in the dimerization mode of inhibition. Atom-based representation of the peptide is shown in default colors and HIV-1 PR monomer conformations are shown in green ribbons.