Figure 1.
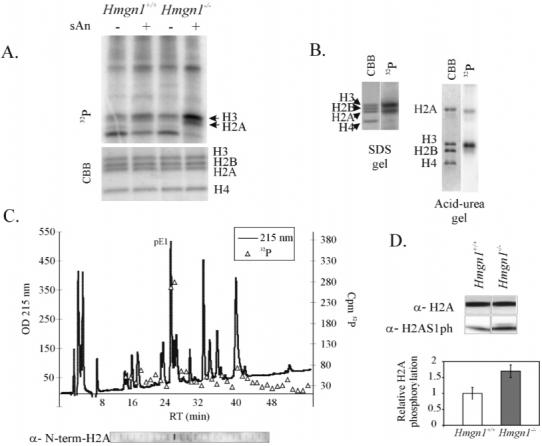
Elevated levels of H2A1ph in Hmgn1-/- cells. (A) Anisomycin-induced phosphorylation of histone H2A occurs in vivo and is affected by loss of HMGN1 protein. Hmgn1+/+ and Hmgn1-/- mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were pulse labeled by 32P and treated with anisomycin. Nuclear proteins were visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining of SDS-PAGE and PhosphoImaging. (B) Msk1 phosphorylates both histones H3 and H2A in nucleosomes. Chicken core particles were phosphorylated using 32P-ATP and Msk1 in vitro and subjected to SDS-PAGE or acid-urea PAGE. Gels were stained by CBB and exposed to PhosphoImager. (C) Msk1 phosphorylates predominantly serine 1 of histone H2A. Labeled histone H2A was isolated and digested with Glu-C, and the resulting peptides were separated by reverse-phase HPLC (215 nm profile is shown). Fractions from HPLC were either counted by liquid scintillation and plotted (32P triangles) or immunoblotted with anti-N-terminal H2A peptide antibodies (panel below the elution profile). pE1 denotes the N-terminal peptide of histone H2A. (D) The level of H2AS1ph is higher in exponentially growing Hmgn1-/- cells. Proteins from Hmgn1-/- and Hmgn1+/+ MEFs were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against histone H2A or against H2AS1ph. The bar graphs represent averages from three independent experiments. H2AS1 phosphorylation signals were normalized to the CBB signals in the corresponding samples.
