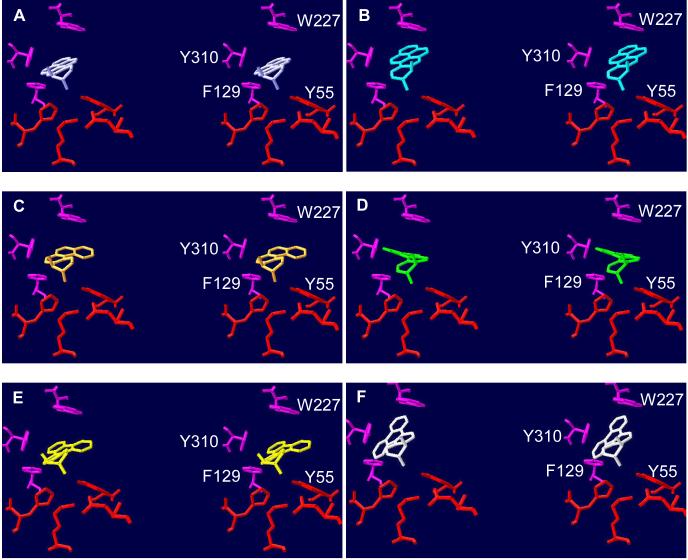
Figure 7.
Docking of PAH trans-dihydrodiols in the active site of AKR1C9. Molecular modeling was carried out using crystal structure 1AFS, the ternary complex of AKR1C9-NADP+-testosterone (48), in Swiss PDB viewer. The stereoisomers of B[g]C-11,12-dihydrodiol were built as described in Figure 6 and manually docked into the active site. Amino acid residues and trans-dihydrodiols are shown in stick representation. The catalytic tetrad is shown in red and other substrate contact residues are shown in magenta. The trans-dihydrodiols are (A) B[a]P-7S,8S-dihydrodiol (lavender), (B) B[a]P-7R,8R-dihydrodiol (cyan), (C) B[c]Ph-3S,4S-dihydrodiol (orange), (D) B[c]Ph-3R,4R-dihydrodiol (green), (E) B[g]C-11S,12Sdihydrodiol (yellow), and (F) B[g]C-11R,12R-dihydrodiol (white). With the exception of B[g]C-11R,12R-dihydrodiol, none of the PAH trans-dihydrodiols clash with active site residues of AKR1C9. The presence of the ring that forms the fjord-region of B[g]C-11R,12R-dihydrodiol causes clashes with active site residues F129, W227, and Y310A (panel F).