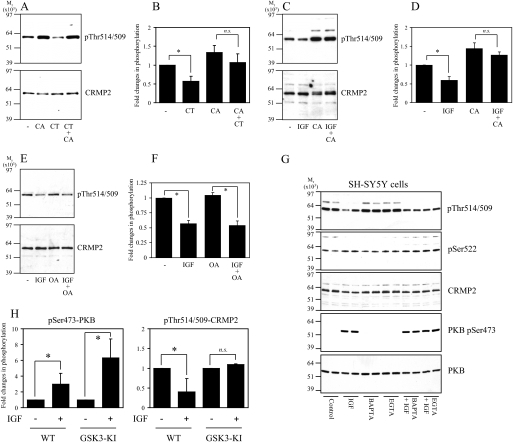
FIGURE 3.
CT99021- and IGF1-induced dephosphorylation of CRMP2 requires PP1 activity. A, SH-SY5Y cells were incubated without (lanes 1 and 3) or with 10 nm calyculin A (lanes 2 and 4) for 15 min followed by the addition of 2 μm CT99021 (CT) for a further 30 min. Cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis using Thr(P)-514/509 (upper panel) and total CRMP2 (lower panel) antibodies. B, the ratio of phospho-CRMP2/total CRMP2 in cells from A (n = 3; n.s., not significant; *, p < 0.05 relative to control (Students t test); average ± S.D.). C, SH-SY5Y cells were incubated without (lanes 1 and 2) or with 10 nm calyculin A (lanes 3 and 4) for 15 min followed by the addition of 50 ng/ml IGF1 (lanes 2 and 4) for a further 30 min. Cell lysates were immunoblotted as described in A. D, the ratio of phospho-CRMP2/total CRMP2 in cells from D (n = 3). E and F, same as C and D except the calyculin A was replaced by 10 nm okadaic acid. G, same as C, except cells were treated in the absence or presence of IGF1 with 10 μm BAPTA-AM or 1 mm EGTA. PKB, protein kinase B. H, primary cortical neurons from wild type or GSK3-knock-in (KI) mice were stimulated with or without 100 ng/ml IGF1 for 1 h, then lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis as described in A. In addition, the membranes were incubated with antibodies that specifically recognize protein kinase B when phosphorylated at Ser-473 or an antibody that recognizes phosphorylated and unphosphorylated protein kinase B equally well (loading control). The phosphorylation level of protein kinase B and CRMP2 is presented relative to unstimulated controls after correction for loading (average ± S.D.; n.s., not significant; *, p < 0.002 relative to control (Student's t test); primary neuron preparations from at least seven different animals for each genotype). WT, wild type.