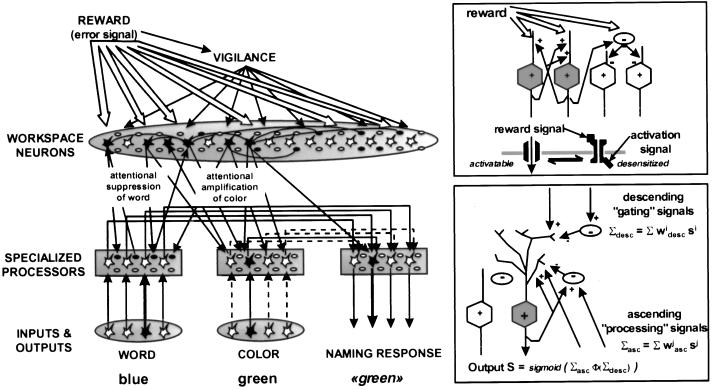
Figure 2.
Architecture of the simulated network. (Insets) The proposed mechanisms for reward-dependent changes in workspace unit activity (Upper) and for the interaction of ascending and descending connections to a given area (Lower). Although each unit in the simulation presumably represents ≈100 neurons in an actual brain, our scheme epitomizes the basic organization of a cortical column, with intra-columnar recurrent excitation, intra-areal and mid-range excitatory connections providing excitation or inhibition (via intermediate processing inhibitory interneurons), and descending excitatory connections providing upward or downward modulation of activity (via intermediate gating inhibitory interneurons). The network is depicted in a state of activity typical of a correct trial in the effortful Stroop task. Attentional amplification reverses the relation between conflicting word and color inputs by amplifying the weaker color unit activity and suppressing the stronger word unit activity.