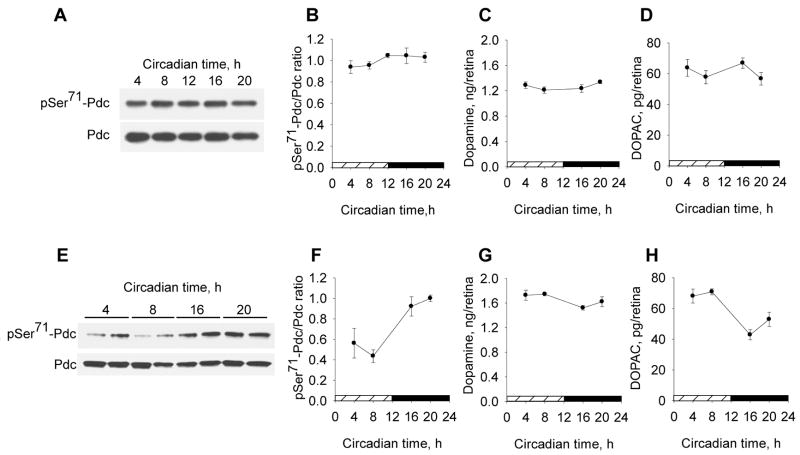
Fig. 6. Circadian rhythms of pSer71-Pdc/Pdc, dopamine, and DOPAC in the retinas of C57Bl/6J and C3H/f+/+ mice.
Retinal concentrations of pSer71-Pdc, total Pdc, dopamine and the dopamine metabolite DOPAC were measured in two strains of mice, C57Bl/6J (A–D) and C3H/f+/+ (E–H), on the second/third day of constant (24h/day) darkness. Two-factor ANOVA shows a significant effect of “circadian time” for C3H/f+/+ mice but not C57Bl/6J mice for pSer71-Pdc/Pdc (n=4–5; p<0.001), dopamine (n=5; p<0.05) and DOPAC (n=5; p<0.001); and significant interactions between factors circadian time and genotype (p<0.05 for pSer71-Pdc/Pdc ratio and dopamine, p<0.001 for DOPAC). A significant negative correlation existed between retinal DOPAC content and pSer71-Pdc/Pdc ratio (Pearson correlation coefficient r = −0.77, p<0.001).