Fig. 4.
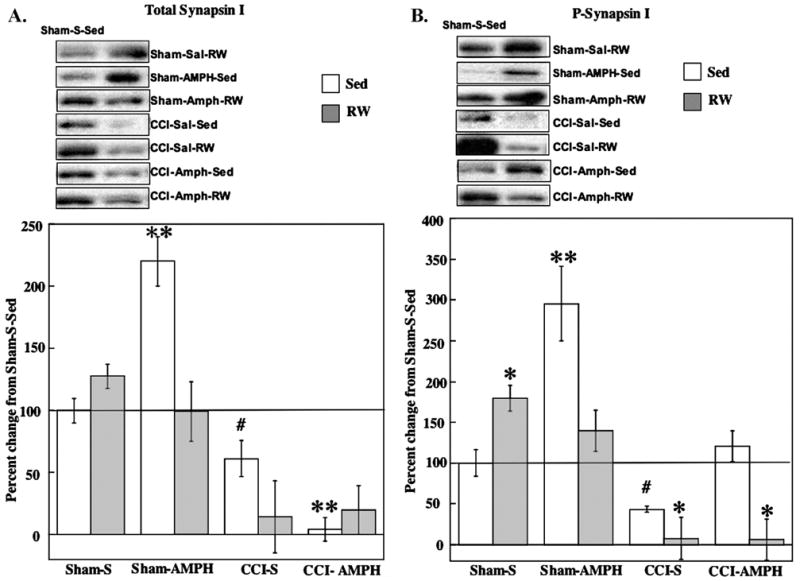
Effects of AMPH treatment and RW exposure on total and P-synapsin I. Panels contain data for all group means±S.E.M. (A) Total synapsin I increased in Sham-AMPH-Sed rats compared with Sham-S-Sed controls. Total synapsin I levels were decreased after CCI injury, with the greatest reductions occurring after AMPH or RW treatments. ** P<0.005 compared with Sham-S-Sed; # P<0.05 compared with CCI-AMPH-Sed. (B) P-synapsin I increased after RW or AMPH treatment alone in Shams compared with Sham-S-Sed. P-synapsin I levels were decreased in CCI-S-RW and CCI-AMPH-RW groups compared with Sham-S-Sed. The CCI-AMPH-Sed treatments increased P-synapsin compared with CCI-S-Sed counterparts. * P<0.05 compared with Sham-S-Sed; ** P<0.005 compared with Sham-S-Sed; # P<0.05 compared with CCI-AMPH-Sed. Representative blots are shown for each experimental group compared with Sham-S-Sed controls (left side blots).
