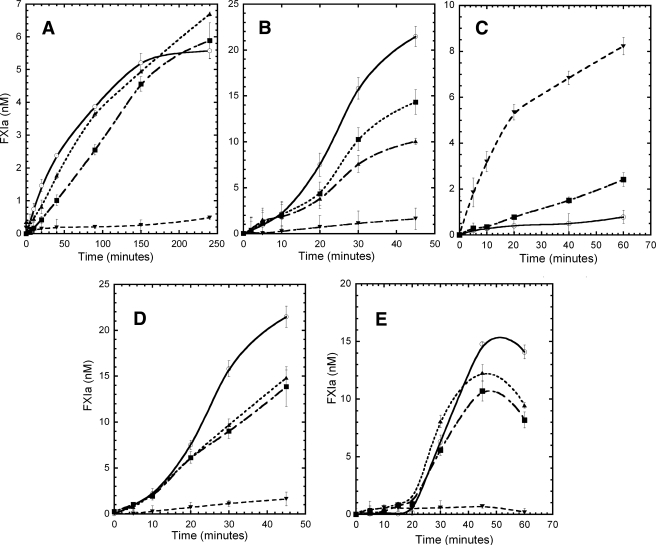
FIGURE 3.
FXI activation by FXIIa and thrombin and autoactivation. A, activation of FXI and the mutants (30 nm) by FXIIa (3 nm) in solution were carried out in TBSA buffer (NaCl 150 mm, Tris-HCl 50 mm, pH 7.4, 0.1% BSA). The incubation mixtures were sampled at the indicated time points; the activity of FXIIa was inhibited by CTI, and the generation of FXIa was determined by its capacity to cleave the synthetic substrate S2366 (330 μm). B, activation of FXI and the mutants (30 nm) by FXIIa (3 nm) was carried out in the presence of 1 μg/ml of dextran sulfate (500 kDa) in TBSA buffer. C, FXIC321S,K331A mutant (30 nm) was activated by FXIIa at different enzyme:substrate molar ratios, 1:10 (○), 1:5 (▪), and 1:1 (▾). The reactions were carried out in TBSA buffer (NaCl 150 mm, Tris-HCl 50 mm,pH 7.4, 0.1% BSA). The FXIIa activity was inhibited by CTI as described under “Experimental Procedures,” and the generation of FXIa was determined by its capacity to cleave the synthetic substrate S2366 (330 μm). D, activation of WTFXI and mutants (30 nm) by thrombin (1 nm) was carried out in the presence of 1 μg/ml of dextran sulfate (500 kDa) in TBSA buffer. The thrombin was inhibited by addition of hirudin (5 nm) as described under “Experimental Procedures,” and the generation of FXIa was determined by its capacity to cleave the synthetic substrate S2366 (330 μm). E, autoactivation of FXI and mutants (30 nm) on dextran sulfate (1 μg/ml, 500 kDa) surface in TBSA buffer (NaCl 150 mm, Tris-HCl 50 mm, pH 7.4, 0.1% BSA). The incubation mixtures were sampled at the indicated time points, and the generation of FXIa was determined by its capacity to cleave the synthetic substrate S2366 (330 μm). Data are shown for activation of WTFXI (○), FXIC321S (▪), FXIC321S,H343A (▴), and FXIC321S,K331A (▾). Results (not shown) for the monomeric mutants FXIC321S,E287A, FXIC321S,I290A, FXIC321S,Y329A, and FXIC321S,L284A were virtually identical to those for FXIC321S,K331A.