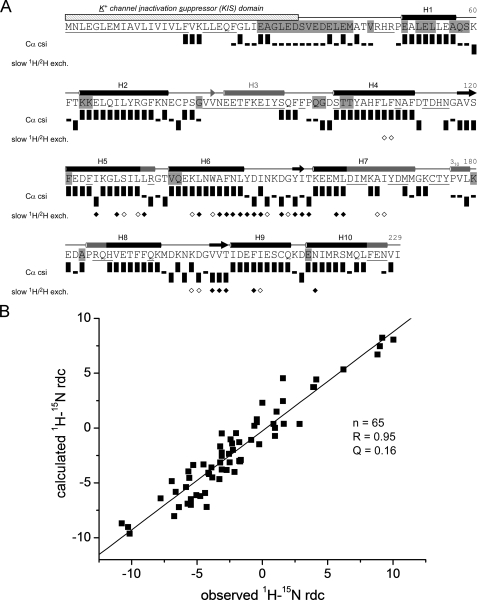
FIGURE 2.
NMR data on secondary structure and tertiary folding of KChIP4a. A, sequence, secondary structure, and schematic representation of NMR data of KChIP4a. The KIS domain is indicated by a hatched bar. Secondary structure elements determined by NMR and for the crystal structure of KChIP1 (5) are indicated by black and gray symbols, respectively. Cylinders represent helices (H1-H10), arrows are short β-strands in the metal-binding loops of the EF-hands. Residues whose backbone amide group was not assigned are underlined; residues not protected from solvent exchange on the ms-s timescale are highlighted in gray. Cα chemical shift index (csi) (38) (values were corrected for 2H isotope effects (48, 49)) identifies secondary structures of KChIP4a: Upright bars reflect a csi value of +1 (typical forα-helices), bars with downward orientation represent a csi value of -1 (typical for β-strands), small black rectangles represent a csi value of 0 (chemical shifts similar to random coil values). Diamonds summarize a 1H/2H exchange experiment: open and filled symbols correspond to residues with amide protons still present after 90 min and 28 h of exchange time in 100% 2H2O, respectively. B, analysis of 1H-15N residual dipolar couplings (RDCs) of KChIP4a. Correlation between observed 1H-15N RDCs and couplings predicted for a structural model of the KChIP4a core based on the 2.3 Å x-ray structure of isolated KChIP1 (5) (PDB entry 1S1E). The analysis was done with the PALES program (26). Alignment tensor relative to the model: DaNH = 6.4 Hz and rhombicity r = 0.35.