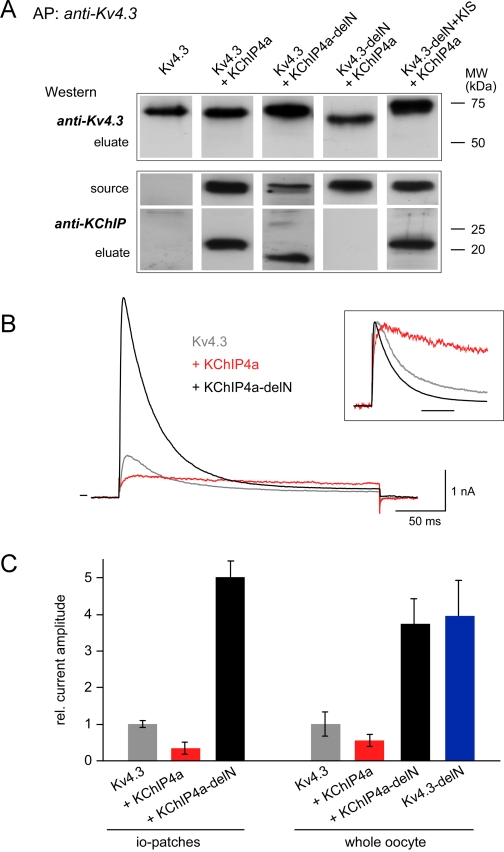
FIGURE 7.
Significance of the helical KIS domain for assembly and surface expression of Kv4.3-KChIP4a complexes. A, formation of Kv4.3-KChIP4a complexes required the core domain of KChIP and a helical segment in the N terminus of Kv4.3. Eluates from affinity purifications (AP) with an anti-Kv4.3 antibody from crude membrane preparations of oocytes co-expressing the indicated proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and Western-probed with anti-Kv4.3 or an antibody targeting the core domain of KChIPs (anti-KChIP). Total amount of protein used for the AP was estimated to equal that of the Kv4.3 protein. Source represents the AP-input Western-probed with anti-KChIP. Molecular weight scales for eluates are as indicated. B, current responses to 250-ms voltage steps from -80 to 50 mV recorded in giant inside-out patches excised from Xenopus oocytes expressing Kv4.3 or co-expressing Kv4.3 and either KChIP4a or the KIS-deleted mutant KChIP4a-delN. Inset, current traces normalized to the peak outward current; timescale is 50 ms. C, bar diagram representing the peak current amplitude recorded from whole oocytes (right panel) or in inside-out patches (left panel) excised from oocytes expressing the indicated channels or channel complexes. Values are mean ± S.D. of 6–8 oocytes or 8 inside-out patches; current amplitudes were normalized to the mean value determined for homomeric Kv4.3 channels. Note the marked increase in current amplitude observed upon deletion of the KIS domain.