Fig. 12. Model for pORF3-mediated ERK activation.
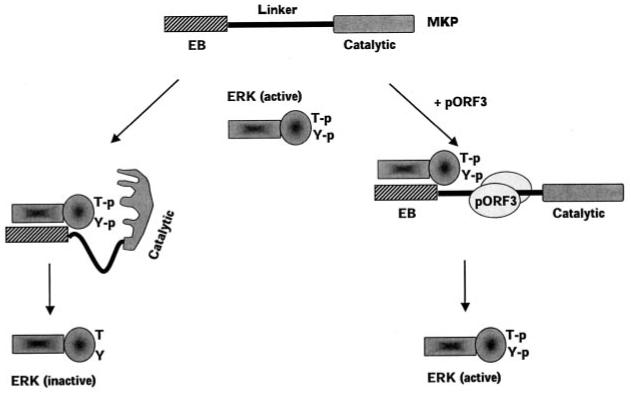
Binding of ERK to the EB domain of MKP-3 leads to a conformational change in the latter bringing its catalytic domain in close proximity to the phosphothreonine (T-p) and phosphotyrosine (Y-p) residues in activated ERK. This leads to dephosphorylation and inactivation of ERK. The ORF3 protein binds the linker region of MKP-3 (possibly as a dimer) and prevents the conformational change required for its activation following ERK binding to the EB domain. This results in catalytically inefficient MKP-3 and higher levels of active ERK.
