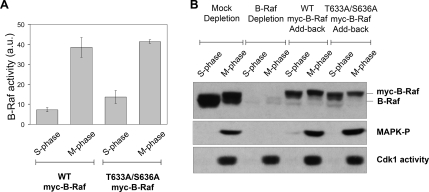
Figure 2.
Mitotic activation of Xenopus 95-kDa B-Raf does not require phosphorylation at conserved Thr-633 and Ser-636 residues. (A) Xenopus nonphosphorylatable B-Raf (T633A/S636A) mutant undergoes activation in M-phase egg extracts. Recombinant myc-tag Xenopus B-Raf proteins (WT or T633A/S636A mutant) were precipitated from B-Raf–depleted S- or M-phase– arrested extracts with a myc-epitope antibody and assessed for B-Raf kinase activity by an in vitro–linked kinase assay. B-Raf activity is expressed in arbitrary units (a.u.) as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Equal loading of myc-B-Raf immunoprecipitates was confirmed by B-Raf Western blotting (not shown). M-phase was confirmed by measuring Cdk1-H1–associated kinase activity. (B) The nonphosphorylatable B-Raf (T633A/S636A) mutant is able to rescue MAPK activation at mitosis in B-Raf–depleted Xenopus egg extracts. Mock, B-Raf–depleted extracts, and B-Raf–depleted extracts supplemented with recombinant WT or T633A/S636A mutant myc-B-Raf (top panel) were driven into mitosis with recombinant nondegradable cyclin B. M-phase egg extracts were confirmed by measuring Cdk1-associated H1 kinase activity (bottom panel). Activation of the MAPK cascade was determined by Western blotting for phospho-MAPK levels (middle panel).