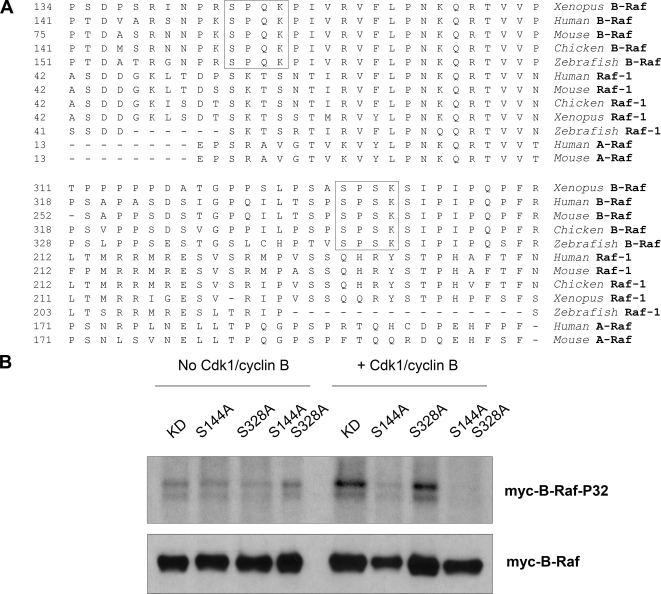
Figure 6.
Cdk1/cyclin B directly phosphorylates Xenopus B-Raf in vitro at a conserved Serine-144 residue. (A) Two putative Cdk phosphorylation sites in Xenopus B-Raf (marked by squares) are conserved in vertebrates for B-Raf but not Raf-1 or A-Raf. The N-terminal portion of amino acid sequences of Xenopus B-Raf (AAZ06667), human B-Raf (P15056), mouse B-Raf (CAB81555), chicken B-Raf (Q04982), zebrafish B-Raf (BAD16728), human Raf-1 (P04049), mouse Raf-1 (NP084056), chicken Raf-1 (CAA30069), Xenopus Raf-1 (P09560), zebrafish Raf-1 (BAD34647), human A-Raf (TVHUAF), and mouse A-Raf (P04627) were aligned by using MegAlign software. (B) Cdk1/cyclin B directly phosphorylates Xenopus B-Raf in vitro at a conserved Serine-144 residue. Immunoprecipitated wild-type (WT) and mutant myc-B-Raf proteins, isolated from S-phase Xenopus egg extracts, were subjected to an in vitro phosphorylation in the absence or presence of purified active Cdk1/cyclin B (New England Biolabs). Phosphorylation of myc-B-Raf proteins was visualized by autoradiography. Myc-tag Western blotting was performed as a loading control.