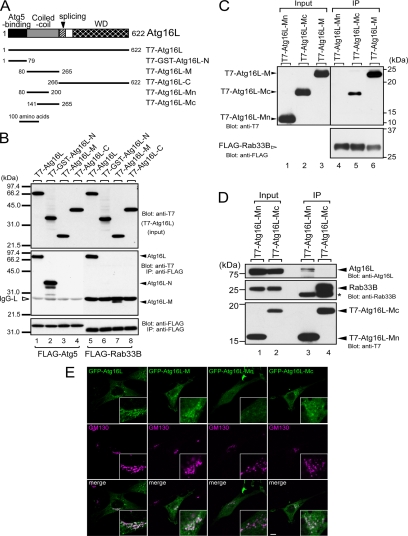
Figure 3.
Rab33B-binding domain of Atg16L. (A) Schematic representation of Atg16L and the truncated mutants used in this study (Mizushima et al., 2003; see text for details). (B) Atg16L interacted with Atg5 via the N-terminal domain (lane 2) and with Rab33B via the coiled-coil domain in the middle of the molecule (lane 7). The binding assays and description of the data are the same as in the legend to Figure 1B. (C) The latter part of Atg16L-M (Atg16L-Mc), not the former part (Atg16L-Mn), interacts with Rab33B. Beads coupled with FLAG-Rab33B were incubated with COS-7 cell lysates containing T7-Atg16L-Mn, T7-Atg16L-Mc, or T7-Atg16L-M. Cell lysates (Input, lanes 1–3) and proteins bound to the beads (IP, lanes 4–6) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti-T7 tag antibody (Blot: anti-T7, top) and HRP-conjugated anti-FLAG tag antibody (Blot: anti-FLAG, bottom). (D) Rab33B-binding site of Atg16L is distinct from the site required for homo-oligomerization. Beads coupled with T7-Atg16L-Mn or T7-Atg16L-Mc were incubated with NIH3T3 cell lysates. Cell lysates (Input, lanes 1 and 2) and proteins bound to the beads (IP; lanes 3 and 4) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti-Atg16L antibody (Blot: anti-Atg16L, top), anti-Rab33B antibody (Blot: anti-Rab33B, middle), and HRP-conjugated anti-T7 antibody (Blot: anti-T7, bottom). The asterisk indicates the light chain of IgG used for immunoprecipitation. (E) Rab33B binding domain of Atg16L is recruited to the Golgi. The NIH3T3 cells transiently expressing GFP-Atg16L, GFP-Atg16L-M, GFP-Atg16L-Mn, or GFP-Atg16L-Mc (green, top) cultured in DMEM were fixed and stained with anti-GM130 antibody (magenta, middle). Merged images are shown in the bottom panels. Bar, 10 μm.