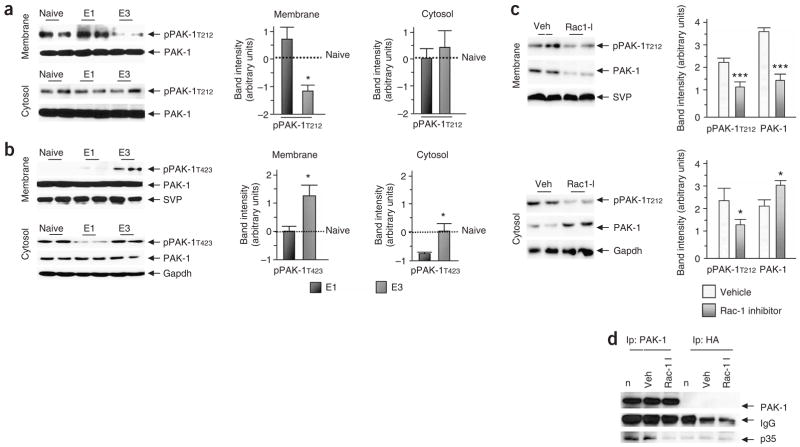
Figure 4.
Inhibition of Rac-1 facilitates extinction. (a) Membrane and cytosolic fractions were prepared from the hippocampus of mice 0.5 h after exposure to E1, E3 or from naive animals and analyzed for PAK-1 by immunoblotting. Levels of PAK-1Thr212 were significantly decreased in the membrane fraction after E3. (b) The same lysates as in a were used to analyze the levels of pPAK-1T423, a non-Cdk5 phosphorylation site that indicates active PAK-1. pPAK-1T423 levels were significantly increased after E3 in the membrane fraction. In the cytosolic fraction, pPAK-1T423 levels decreased after E1 when compared with naive mice, but increased back to baseline levels after E3. (c) Hippocampal cytosolic and membrane fractions were prepared on E3 0.5h after mice were injected (ICV) with either vehicle or Rac-1 inhibitor. Immunoblot analysis showed a significant reduction of membrane-associated p35/Cdk5, pPAK-1T212 and PAK-1 levels. (d) The same lysates as described in c were used to immunoprecipitate PAK-1. A hemagglutinin antibody served as a control for nonspecific binding of proteins to the protein A–agarose beads. The precipitates were immunoblotted with antibodies to PAK-1 and p35. There was a substantial reduction in the amount of p35 that co-immunoprecipitated with PAK-1 in lysates from mice that were administered with Rac-1 inhibitor. Error bars represent s.e.m.