Figure 2.
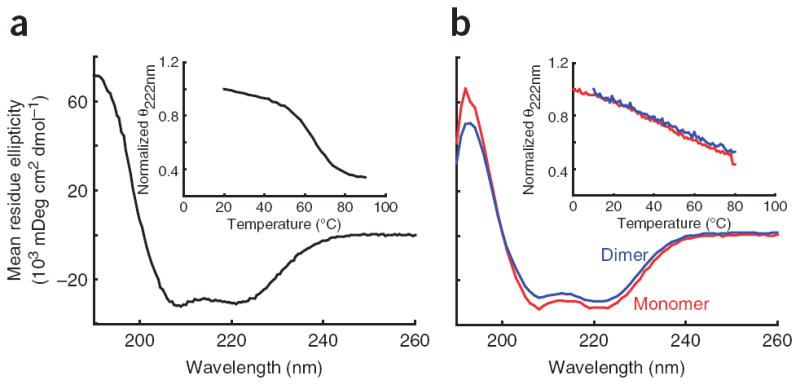
CD spectra for the PT and MT-DT domains. (a) A typical CD spectrum of the PT showing the characteristic double minima of an α-helical protein. Inset, the thermal melt of the PT showing the cooperative melt typical of a folded protein. (b) CD spectra of the MT-DT as a monomer (red) or as an artificial dimer held together by a C-terminal disulfide bridge (blue). Inset, thermal melt curves showing that both constructs have a broad thermal unfolding transition as expected for a single α-helix. The similarity of the spectra and melt curves of the monomer and dimer indicates that no structural changes occur when the MT-DT is placed in conditions mimicking high concentrations. This indicates an inability of the MT-DT to dimerize.
