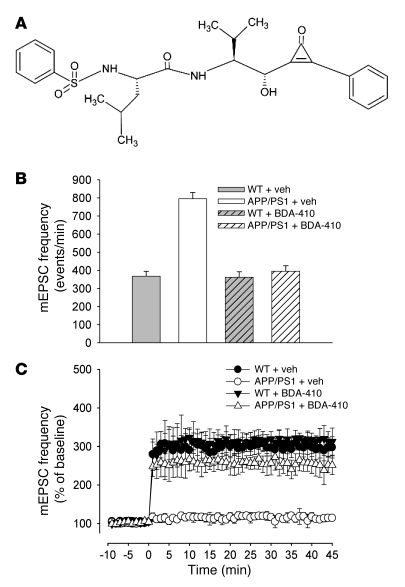
Figure 2. The highly selective calpain inhibitor BDA-410 reestablished normal basal frequency of spontaneous neurotransmitter release and rescued impairment of synaptic plasticity in APP/PS1 mouse cultures.
(A) Chemical structure of BDA-410. (B) Vehicle-treated APP/PS1 cultures showed approximately 2-fold increase of spontaneous mEPSC frequency (n = 7) compared with vehicle-treated WT cultures (n = 8; P < 0.01 with 1-way ANOVA). BDA-410 did not affect average basal mEPSC frequency in WT cultures (n = 7) and reestablished normal basal frequency of spontaneous neurotransmitter release in APP/PS1 cultures (n = 8; P < 0.01). (C) Application of glutamate (200 μM) did not enhance mEPSC frequency in cultures from APP/PS1 mice compared with cultures from WT mice (n = 7 in APP/PS1 cultures; n = 8 in WT littermate cultures; P < 0.01 with 2-way ANOVA). mEPSC amplitude values were not affected by glutamate (data not shown). Block of calpain activity through BDA-410 was beneficial against the impairment of long-lasting enhancement of synaptic transmission (n = 8; P < 0.01 compared with vehicle-treated APP/PS1 cultures), without affecting it in WT cultures (P > 0.05 compared with vehicle-treated WT cultures).