Fig. 2.
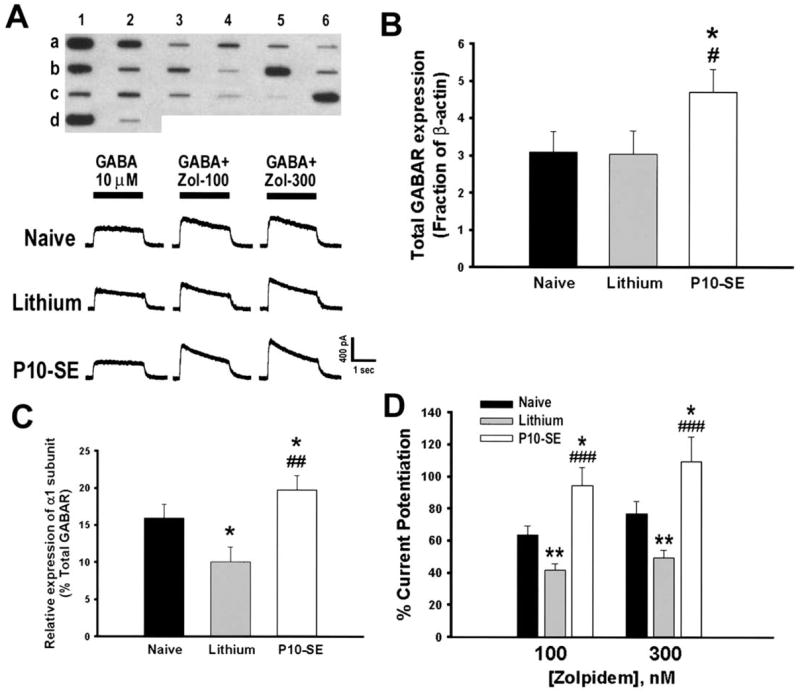
P10-SE altered GABAR subunit expression and pharmacology. (A) Top panel: Representative reverse northern blot from a single DGN isolated from a P10-SE rat. The slot-blot contains cDNAs encoding GABAR subunit α1–α6 (a1–6), β1–β3 (b1–3), γ1–γ3 (b4 – 6), δ, ε, π and θ (c1–4), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP; c5), neurofilament-L (NF-L, c6), β-actin (d1), pBluescript (d2). Bottom panels: Representative responses to 10 μM GABA application alone and co-application with zolpidem (100 and 300 nM) in DGNs isolated from naive control, lithium control and P10-SE rats. (B) Total GABAR mRNA expression was increased in P10-SE rats compared with controls (effect of group: F=3.11; P=0.04; pair-wise comparison to naive * P<0.05, lithium # P<0.05, SAS Proc Mixed models; n=21 cells total from nine rats for P10-SE [1–4 cells/rat]; 24 cells total from eight rats for naive-controls [1–6 cells/rat]; 18 cells total from eight rats for lithium-controls [1–4 cells/rat]). (C) Relative expression of α1 subunit mRNA was increased in DGNs from P10-SE rats compared with controls (effect of group: F=7.28; P=0.001; pair-wise comparison to naive * P<0.05, lithium ## P<0.01, SAS Proc Mixed models). (D) GABA current potentiation by zolpidem, a BDZ1 receptor specific positive modulator, was significantly increased in DGNs from P10-SE rats compared with DGNs from naive or lithium control rats. Each cell was treated with 100 nM and 300 nM zolpidem which was pre-applied alone for 30 s before co-applying drug with 10 μM GABA for 2 s. Cells were washed with drug-free recording solution for 2 min between applications to reduce the effects of current run-down and/or desensitization (* P<0.05, ** P<0.01 compared with naive; ### P<0.001 compared with lithium; one-way ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer test for pair-wise post hoc comparison; n=18 cells from four rats for P10-SE, 31 cells from seven rats for lithium-controls and 15 cells from three rats for naives). Note also handling-induced differences in α1 mRNA expression and zolpidem potentiation between lithium- and naive-control groups as has been previously reported (Hsu et al., 2003).
