Figure 3.
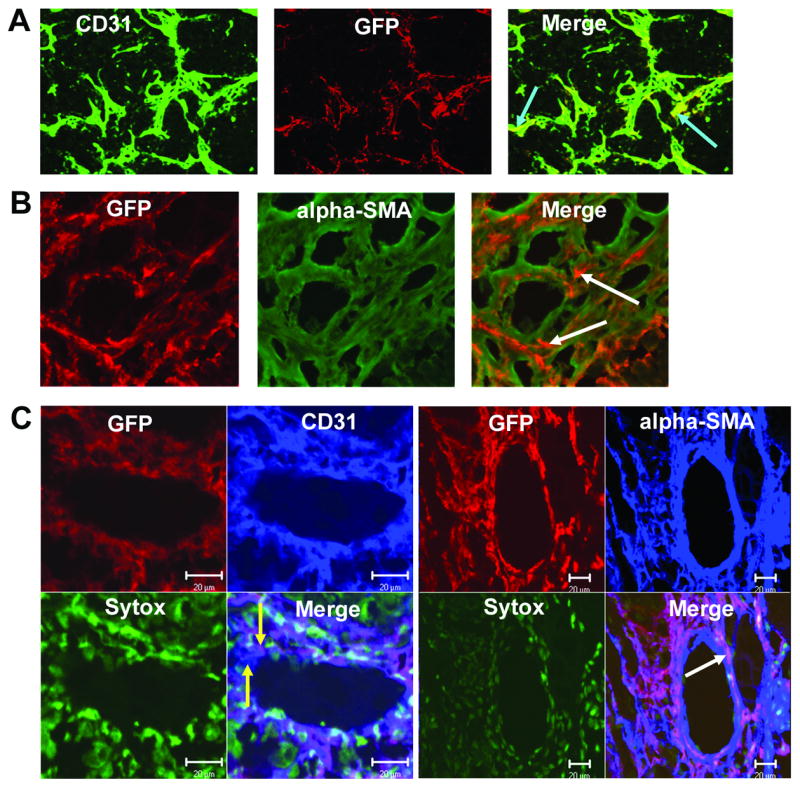
VEGFR2+ and Sca1+/Gr1+ cells differentiate into both endothelial cells and pericytes within the TC71 vasculature. Gfp+ VEGFR2+ and Sca1+/Gr1+ cells were i.v.-injected into nude mice with TC71 tumors. (A) VEGFR2+ cells differentiated into CD31+ endothelial cells (arrows). (B) Confocal microscopy (20×); VEGFR2+ cells also differentiated into α-SMA+ pericytes (arrows), adjacent to locally-derived cells (green) within the vascular smooth muscle cell network. (C) Confocal microscopy; Left (40×): Sca1+/Gr1+-derived cells differentiated into CD31+ endothelial cells that were incorporated into the vascular endothelial lining; yellow arrows indicate adjacent locally-derived (blue) and Sca1+-derived (purple) endothelial cells within the mosaic vessel. Right (20×): Sca1+/Gr1+ cells also differentiated into α-SMA+ cells that comprised the pericyte network (arrow). Sytox was used to stain nuclei green.
