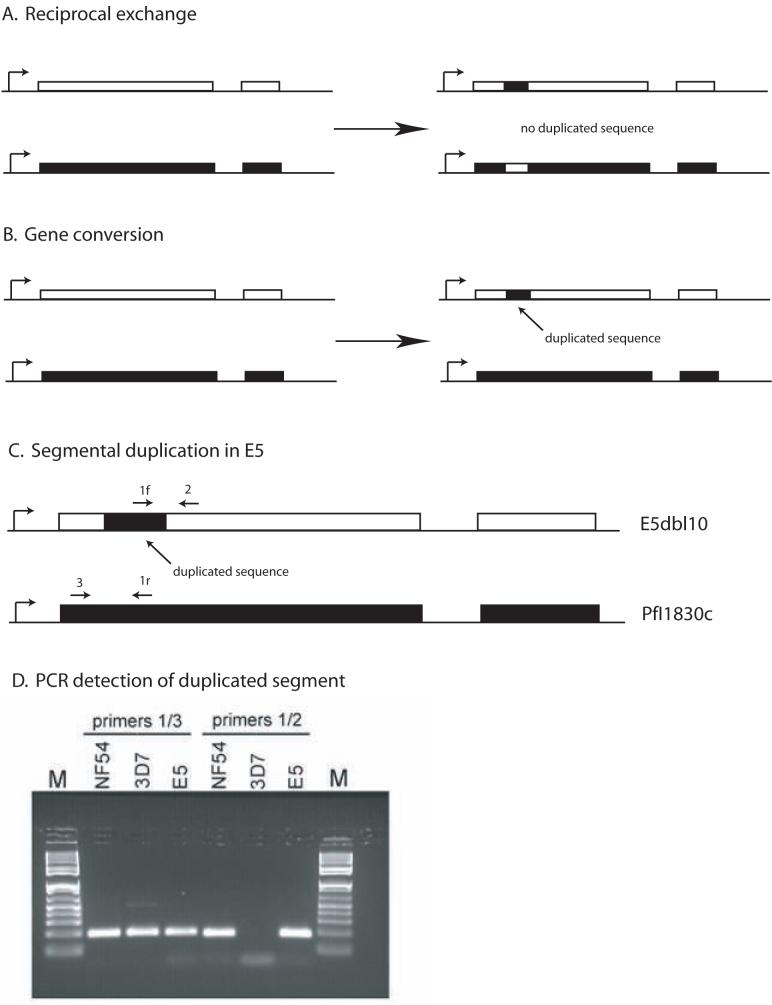
Figure 5.
Schematic showing the results of reciprocal exchange or gene conversion. The genes shown display the two exon structure typical of var genes, with the promoter denoted by a bent arrow. A. Reciprocal exchange results in changes in both genes, but does not lead to either duplication or deletion of any sequences. B. Gene conversions, also referred to as duplicative transpositions, result in the duplication of a stretch of sequence, which then replaces a similar sequence in a related gene, leading to a corresponding deletion. C. Schematic of the duplication of a segment of the var gene PfI1830c into a different var gene within the genome of E5. The positions of gene specific primers that can be used to detect the duplication event are shown and numbered 1-3. Primer 1f and primer 1r are reverse complements and thus function as primers in opposite orientations. D. Ethidium bromide stained agarose gel showing PCR detection of the duplicated segment of PfI1830c. Primer pair 1/3 detects the original PfI1830c gene in NF54, 3D7 and E5 while primer pair 1/2 detects the duplicated segment in NF54 and E5, but not in 3D7.