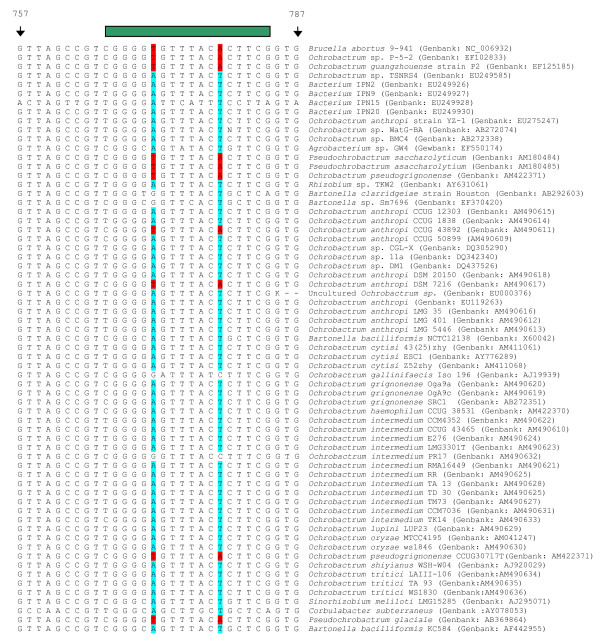
Figure 4.
Alignments of various 16SrRNA sequences around the location of the 16S rRNA771/778 probes. Alignments of fragments of 16S rRNA centred around SNPs at bases 771 and 778 relative to B. abortus 9–941, used in combination with the 16S rRNA1055 SNP to separate Brucella from closely related bacteria. The alignment contains 65 sequences taken directly from Genbank and includes many examples of Ochrobactrum, the closest phylogentic neighbour of Brucella as well as other, less-closely related, members of the α-proteobacteria. In this figure, the targetted Brucella specific SNPs are highlighted in red and the non-Brucella alternatives in blue. The green bar above both figures represents the location of probe hybridisation. The alignment includes only one Brucella sequence as there is 100% identity in the 16SrRNA sequences between all Brucella [34]. Using this assay on its own will discriminate most but not all of the non- Brucella shown from Brucella organisms.