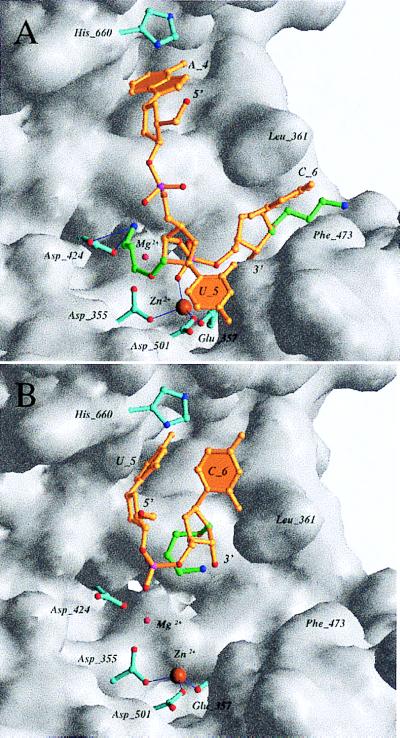
Figure 6.
The two orientations and resulting interactions of AP(AUC)-3′ at the wt-KF exonuclease active site. (A) The positively charged nitrogen of the AP substituent of U5 is hydrogen-bonded to the carboxyl group of D424 and interferes with the binding of the B site metal ion. This ion is absent in the structure, but its normal location is indicated by a small pink sphere labeled Mg2+. (B) Alternative orientation of the modified hexamer with only two residues bound at the active site and loss of coordination between the phosphate group and the Zn2+ ion. The AP(AUC) and AP(UC) fragments are shown as stick models in yellow and atoms of phosphate groups are colored red and magenta for oxygen and phosphorus, respectively. Carbon atoms of the AP substituents of residues U5 and C6 are highlighted in green, and side-chain carbon, nitrogen and oxygen atoms of key amino acids are highlighted in cyan, blue, and red, respectively.