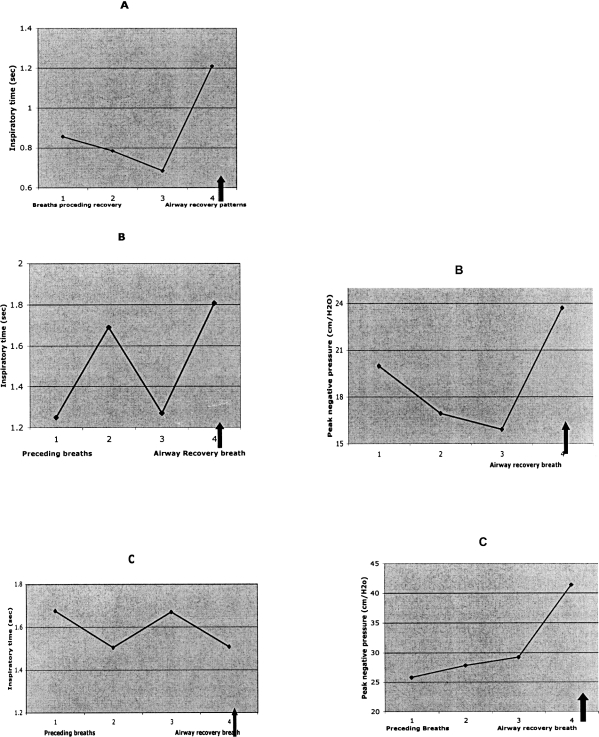
Figure 8.
Data taken from tracings of adult OSA episodes and recovery from obstruction indicating similarities to findings in infants.
A. Note inspiratory time for the recovery breath is much longer than preceding respiratory efforts. The recovery breath was distinctly biphasic, as in infants. Inspiratory peak pressures are not given because the pressure scale went off in the recovery breath. (Data extracted from ref # 17, Fig. 2).
B. Note the increased duration as well as peak inspiratory pressure of the recovery breath. (Data extracted from ref # 5, Fig. 4b).
C. In this example inspiratory time of recovery breath was not prolonged, but inspiratory pressure was distinctly elevated over that of preceding breaths. (Data extracted from ref # 5, Fig. 1a).