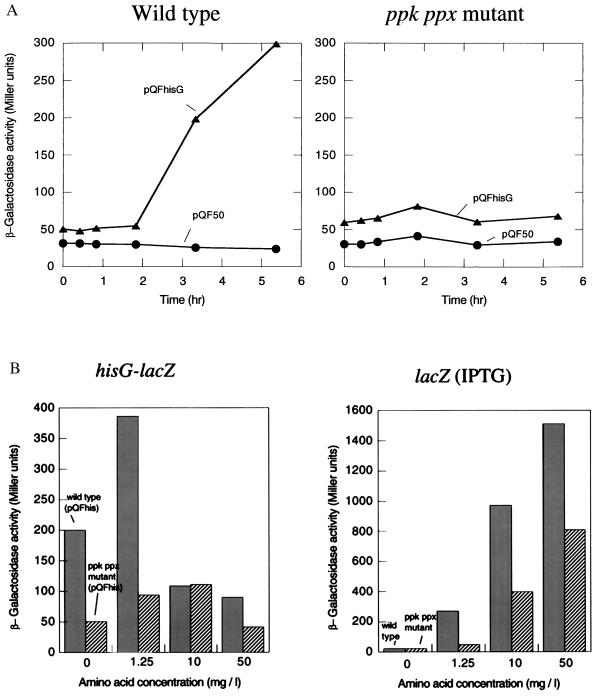
Figure 6.
Induction of β-galactosidase during the nutritional downshift. (A) β-galactosidase activities from the hisG-lacZ fusion were measured in the wild type (Left) and the mutant (Right) harboring pQFhis (the hisG-lacZ fusion), respectively. Strains harboring pQF50 (a promoterless lacZ vector) were used as a control (circle). (B) Effects of amino acid supplementation on β-galactosidase production. The wild type (filled bar) and the mutant (striped bar) were downshifted to the Mops medium supplemented with all 20 amino acids at concentrations of 0, 1.25, 10, and 50 mg/liter, respectively. The left panel shows β-galactosidase activities in strains harboring pQFhis. The right panel indicates β-galactosidase activities from the chromosomal lacZ gene in the wild type and the mutant. The chromosomal lacZ gene was induced by adding isopropyl-1-thio-β-d-galactoside (1 mM) to the Mops medium. β-galactosidase activities were measured 3 hr after the nutritional downshift.