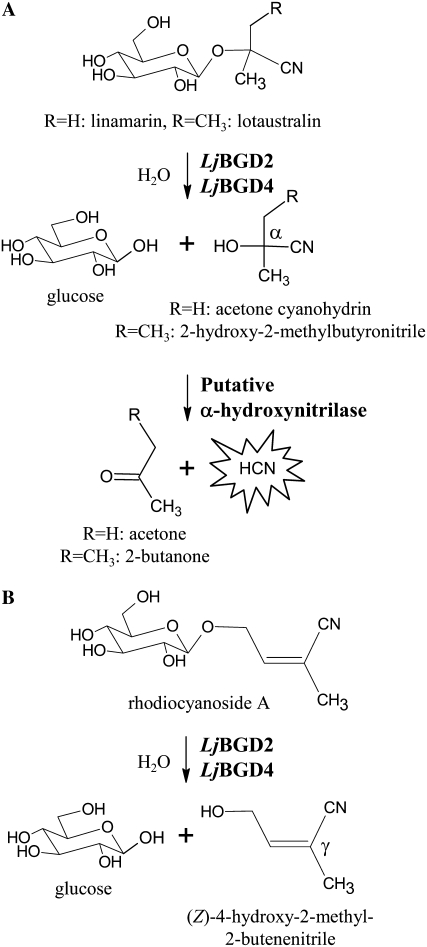
Figure 1.
Bioactivation of lotaustralin, linamarin, and rhodiocyanoside A in L. japonicus leaves. A, Cyanogenic glucosides are β-glucosides of α-hydroxynitriles. Upon cell disruption, β-glucosidases catalyze the hydrolysis of the O-β-glucosidic bond to yield Glc and an α-hydroxynitrile aglucone. The α-hydroxynitrile either spontaneously or enzymatically breaks down to liberate a ketone and toxic HCN. B, Rhodiocyanosides are β-glucosides of β- or γ-hydroxynitriles. In contrast to α-hydroxynitrile glucosides, aglucone formation is not accompanied by the release of HCN.