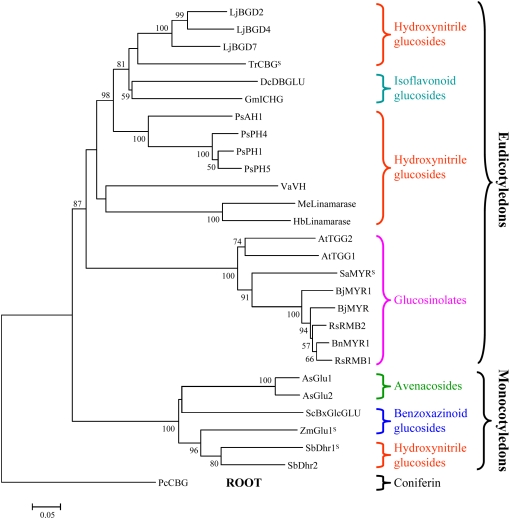
Figure 7.
Phylogenetic analysis of selected plant β-glucosidases involved in the bioactivation of defense compounds. The phylogenetic tree includes hydroxynitrile and isoflavonoid glucoside-cleaving β-glucosidases from eudicotyledons, glucosinolate-degrading myrosinases (Brassicales), and selected β-glucosidases involved in the bioactivation of defense compounds in monocotyledons. The defense compounds degraded are indicated for the different groups of β-glucosidases. “S” indicates enzymes for which the crystal structures have been solved. LjBGD2, LjBGD4, and LjBGD7, L. japonicus β-glucosidases (this study); TrCBG, T. repens cyanogenic β-glucosidase (Barrett et al., 1995); GmICHG, G. max isoflavone conjugate-hydrolyzing β-glucosidase (Suzuki et al., 2006); DcBDGLU, D. cochinchinensis dalcochinase (Cairns et al., 2000); PsAH1, PsPH1, PsPH4, and PsPH5, P. serotina amygdalin hydrolase and prunasin hydrolase isoenzymes (Kuroki and Poulton, 1987; Zheng and Poulton, 1995; Zhou et al., 2002); VaVH, Vicia angustifolia vicianin hydrolase (Ahn et al., 2007); MeLinamarase, M. esculenta linamarase (Hughes et al., 1992; Keresztessy et al., 2001); HbLinamarase, H. brasiliensis linamarase (Selmar et al., 1987); AtTGG1 and AtTGG2, Arabidopsis myrosinases (Barth and Jander, 2006); SaMYR, Sinapis alba (white mustard) myrosinase (Burmeister et al., 1997); BjMYR and BjMYR1, Brassica juncea (mustard greens) myrosinases (Heiss et al., 1999); RsRMB1 and RsRMB2, Raphanus sativus (radish) myrosinases (Hara et al., 2000); BnMYR1, Brassica napus (rape) myrosinase (Chen and Halkier, 1999); As-Glu-1 and As-Glu-2, A. sativa avenacosidases (Gusmayer et al., 1994; Kim et al., 2000); ScBxGlcGLU, S. cereale DIBOA-Glc β-glucosidase (Nikus et al., 2003); Zm-Glu-1, Z. mays glucosidase 1 (Czjzek et al., 2001); SbDhr1 and SbDhr2, S. bicolor dhurrinases (Hösel et al., 1987; Verdoucq et al., 2004); PcCBG, Pinus contorta (lodgepole pine) coniferin β-glucosidase (Dharmawardhana et al., 1995, 1999). The bootstrapped neighbor-joining tree was built in MEGA 4.0 (Tamura et al., 2007). The tree was bootstrapped with 1,000 iterations (node cutoff value, 50%). The underlying amino acid sequences in fastA format and the multiple alignment can be accessed at http://www.p450.kvl.dk/VintherMorant_etal_Figure7.tfa and http://www.p450.kvl.dk/VintherMorant_etal_Figure7_Alignment.pdf, respectively. The phylogenetic tree was rooted using PcCBG as an outgroup. For the bootstrap analysis, 1,000 trials were performed, and the bootstrap values are shown in percentages; bootstrap node values below 50% are not shown. A more elaborate phylogenetic analysis of plant β-glycosidases, including those presented here, is available at http://www.p450.kvl.dk/BGD.shtml.