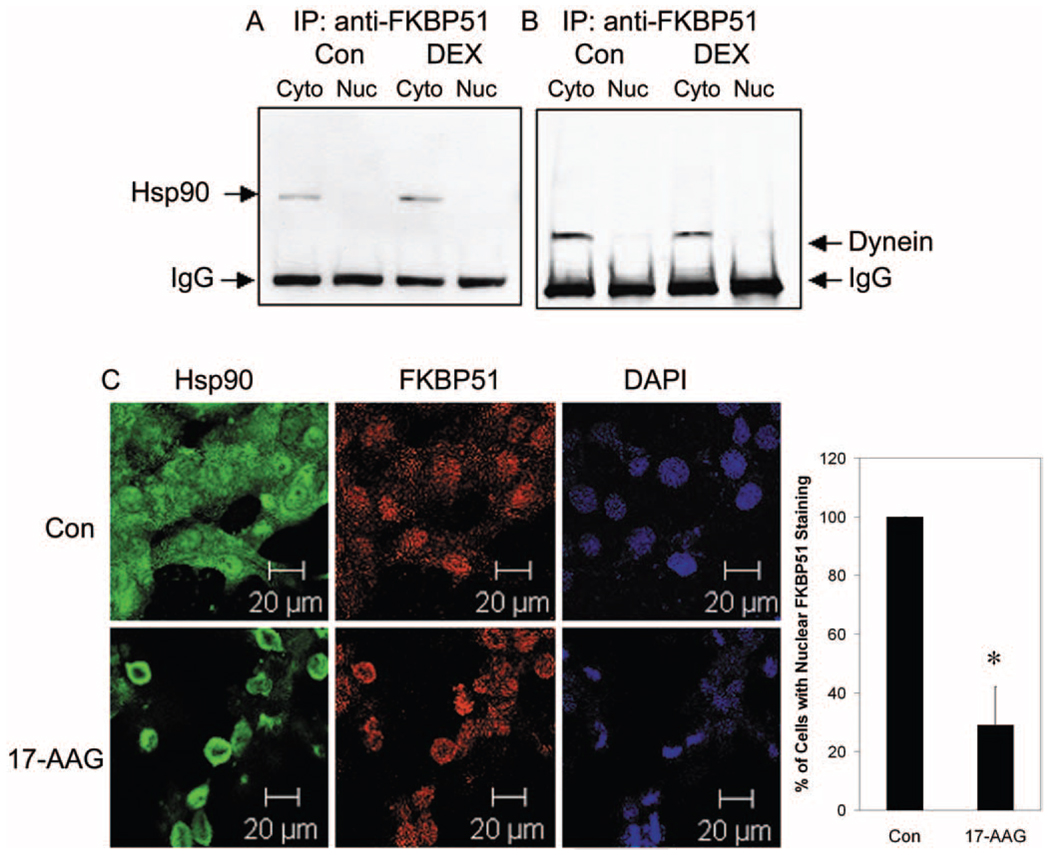
FIGURE 2.
Immunoprecipitation and colocalization of FKBP51 with Hsp90 and dynein in NTM-5 cells. Confluent NTM-5 cells were treated with vehicle (ethanol) or 100 nM DEX for 30 minutes. The cytoplasmic (Cyto) and nuclear (Nuc) fractions were isolated. Cytoplasmic (100 µg) and nuclear (50 µg) proteins were subjected to coimmunoprecipitation with anti-FKBP51 antibody and proteins resolved by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide 4% to 15% gradient gels followed by Western immunoblot analysis with (A) anti-Hsp90 antibody or (B) anti-dynein antibody. (C) Subconfluent (80%–90% confluence) NTM-5 cells were treated with either vehicle control (ethanol) or 1 µM 17-AAG (a specific Hsp90 inhibitor) for 24 hours. The cells were incubated with primary mouse anti-Hsp90 antibody and rabbit anti-FKBP51 antibodies, followed by Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse and Alexa Fluor 633 goat anti-rabbit secondary antibodies. Confocal microscopy was used to detect Hsp90 (green), FKBP51 (red), and DAPI nuclear staining (blue), as labeled. The ratio of the number of cells with nuclear FKBP51 staining versus the total number of cells imaged is represented as the mean percentage ± SEM of results. *P < 0.05 17-AAG vs. vehicle control by t-test; n = 3. Scale bars, 20 µm.