Fig 1. Analyses of two hES cell clones lacking GPI-anchored proteins (GPI-APs).
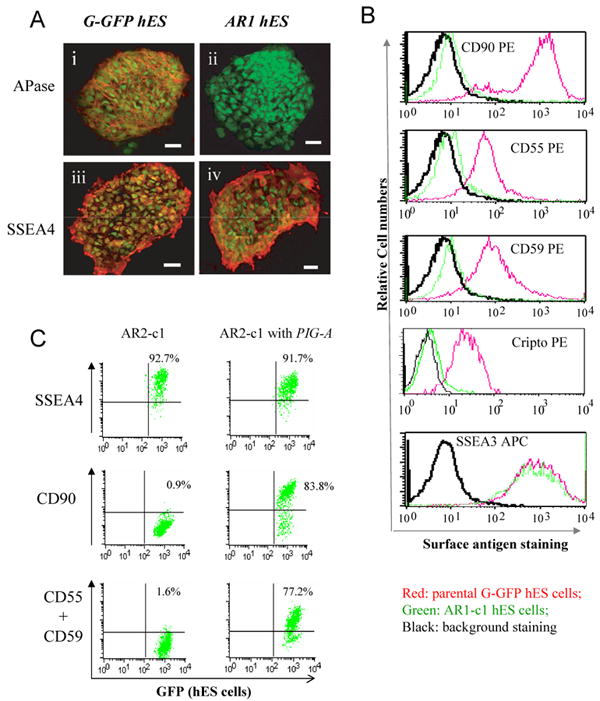
After aerolysin selection, G-GFP derived hES cells that lacked GPI-APs were sorted and expanded. 6 clones were obtained from two large-scale experiments. Two (AR1-c1 and AR2-c1) were further characterized since they can form undifferentiated colonies (Supplement Table S2). (A). Cell surface staining for alkaline phosphatase (APase). The AR1-c1 or its parental G-GFP hES cells (both constitutively expressing GFP) were cultured under a feeder-free condition and fixed before cell surface staining. Mouse monoclonal IgG recognizing either the APase (i and ii) or SSEA-4 (iii and iv) was used as primary antibodies. Then Alexa 555-conjugated antibodies recognizing anti-mouse IgG were used to light up detected antigens. The micrographic images of stained were superimposed with that of cellular GFP signals. While both APase and SSEA4 were detected on cell surface of G-GFP cells (i and iii), only SSEA-4 (iv) but not the APase (ii) was detected on AR1-c1 cells. (B). Flow cytometric analysis of other GPI-APs such as CD90, CD55, CD59 and Cripto using PE-conjugated specific IgGs. The red lines represent staining profiles of the G-GFP control whereas the green lines represent the AR1-c1 hES cells. The black lines represent the background staining (using an irrelevant antibodies). The both hES cell types expressed a high level of surface marker SSEA3. (C). Similar analysis of the AR2-c1 hES cell clone before or after transduction by a lentiviral vector expressing a PIG-A transgene. AR2-c1 cells express SSEA4, but lack CD90, CD55 or CD59. After one round of transduction, ∼80% AR2-c1 cells stably expressed GPI-APs.
