Fig 4. BMP4 induced trophoblast differentiation of normal G-GFP hES cells, but not AR1-c1 hES cells lacking GPI-APs.
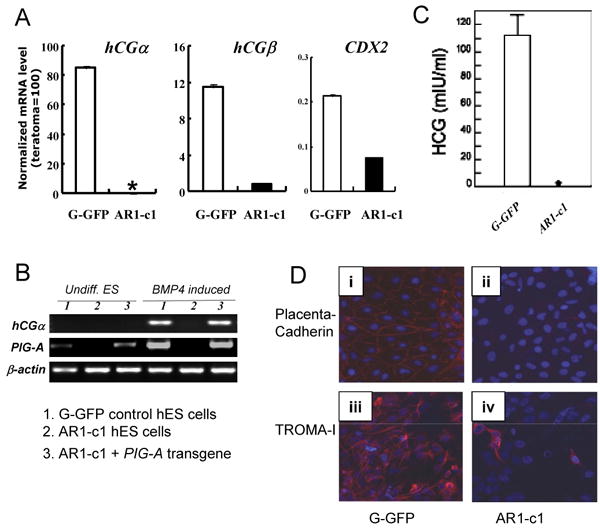
The parental (G-GFP) and AR1-c1 hES cells were cultured under a feeder-free condition and treated with BMP4 (50 ng/ml) for 10 days. Then cells were harvested for RT-PCR analyses (A and B) after the conditioned medium was collected and used to detect hCG hormone by ELISA (C). (A). Quantitative RT-PCR for trophoblast markers such as hCGα, hCGβ and CDX2. * undetectable as in undifferentiated hES cells after 40 cycle PCR. Profiles of the gene expression of other markers (such as NANOG, AFP, CD34 and PAX6) after BMP4 induction are shown in Supplement Fig S3. (C). Conventional RT-PCR using a different primer set for hCGα (as in Fig 3D) and a specific primer set for PIG-A as in Fig 2A. RNA from undifferentiated ES cells (undiff. ES) or after BMP4 induction (BMP4 induced) from either G-GFP (samples 1) or AR1-c1 (samples 2) hES cells was used. In addition, we also included AR1-c1 derivatives in which a PIG-A transgene is expressed (samples 3) in this experiment. (D). immuno-fluorescent staining for trophectoderm markers placenta-cadherin (upper row, i-ii) and TROMA-I (lower row, iii-iv) from the differentiated G-GFP (left) and AR1-c1 cells (right), 11 days after BMP4 induction. The presence of antigen is visualized by anti-mouse IgG conjugated with Alexa 595 (red) and nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue). While the trophectoderm marker induction is obvious in the differentiated G-GFP cells, it is much lower in the GPI-AP deficient AR1-c1 cell population.
