Fig 5. BMP signaling activation is significantly reduced in AR1-c1 hES cells due to the PIG-A and GPI-AP deficiency.
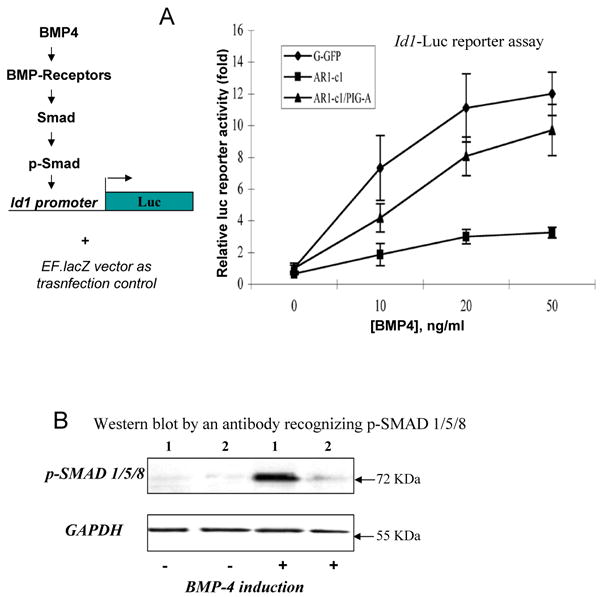
(A). BMP4 signaling activation in G-GFP or AR1-c1 hES cells was measured by a Luciferase reporter (Id1-Luc) controlled by the Id1 gene promoter. Six hours after transfection of the reporter plasmid, cells were stimulated with various concentration of BMP4 for 20 hours and harvested. The Id1-Luc activity was measured, normalized, and calculated relative to that of G-GFP without BMP4 stimulation (defined as 1). The normalized mean and SD (n≥5) were plotted. In one experiment, the Id1-Luc activity in AR1-c1 hES cells that have been transduced with PIG-A transgene was also measured before and after BMP induction (n=5). Combined from two experiments (Σn=7), the mean of the reconstituted AR1-c1/PIG-A cells is statistically greater than the AR1-c1 cells (p<0.05) and insignificant from G-GFP hES cells (p>0.05). (B). Western blot to detect the phosphorylated (activated) form of 3 highly related SMAD proteins (1/5/8) without or with BMP4 induction. G-GFP (1) or AR1-c1 (2) hES cells were treated with BMP4 for 6 hours, and cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting, using purified specific antibodies recognizing the phosphorylated SMAD1/5/8. After stripping, the blot was re-probed by a specific antibody recognizing the housekeeping protein GAPDH.
