Fig. 2.
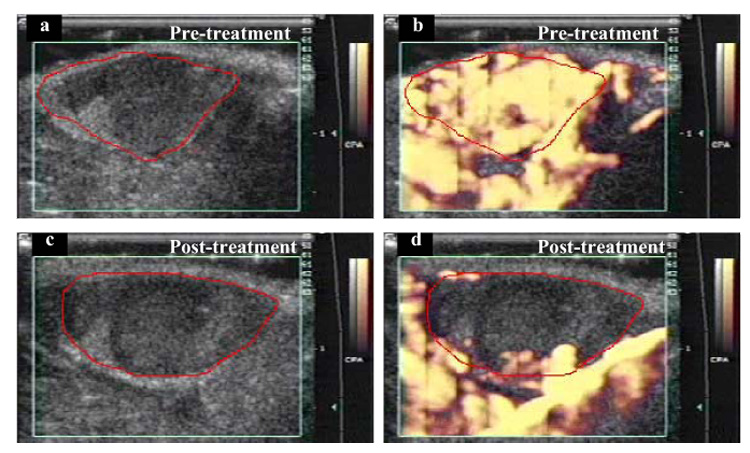
Power Doppler images of a subcutaneous melanoma in a mouse. In the initial pretreatment image (a), the boundary of mostly hypoechoic tumor has been traced in red. The green box superimposed on the image is the region from which Doppler information was acquired (on right side of image are time-gain compensation numbers, centimeter scale and grey-scale and color scale bars). CPA = “color power angio.” (b) At peak enhancement after IV injection of an US contrast agent. (c) Posttreatment (3 min at 2.28 W cm−2), before contrast injection, tumor is again mostly hypoechoic. (d) After contrast injection, there is almost no tumor enhancement, but vascular perfusion is still visible in surrounding healthy tissue. Comparing (b) and (d), it appears that the effect of insonation was to reduce access of contrast medium to tumor blood vessels, but access was maintained in the blood vessels in surrounding healthy tissues.
