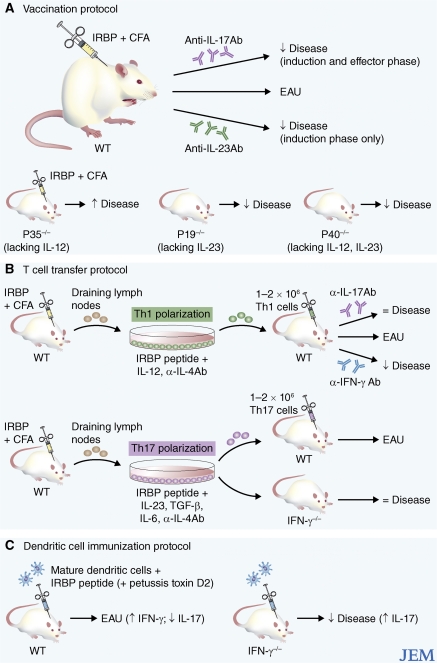
Figure 1.
Th17 or Th1 cells can induce EAU depending on the method of disease induction. (A) Direct vaccination model. Disease was induced by immunizing mice with IRBP plus CFA. There was a significant reduction of EAU in p19 and p40 knockout mice, with a significant increase in EAU in p35 knockout mice compared with wild type. Antibody blockade of IL-17 reduced disease when given either during disease induction or after disease onset, whereas antibody blockade of IL-23 reduced disease only when administered during disease induction. (B) T cell transfer model. Transfer of Th1-polarized, IRBP-specific CD4+ T cells induced EAU (top). In this model, blocking IL-17 had no effect on disease and blocking IFN-γ ameliorated disease. Transfer of Th17-polarized, IRBP-specific CD4+ T cells induces EAU (bottom), and, in this model, disease was equivalent when cells were transferred into IFN-γ–deficient mice. (C) Dendritic cell immunization protocol. IRBP-pulsed mature dendritic cells were injected into mice, followed by pertussis toxin at day 2. In this model, disease was decreased in IFN-γ–deficient mice, despite an increased production of IL-17 in the central nervous system as compared with wild-type mice.