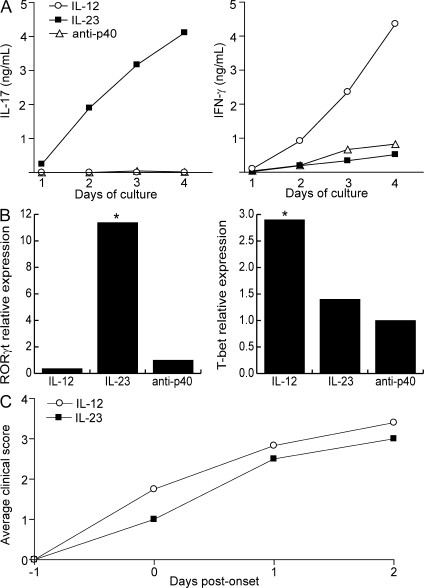
Figure 1.
IL-12– and IL-23–modulated myelin-specific T cells induce EAE in naive hosts. (A) PLP139–151/IFA-primed T cells were cultured with antigen under conditions favorable to the generation of Th1 cells (IL-12, IFN-γ, αIL-4, and αIL-23p19), Th17 cells (IL-23, IL-1, αIFN-γ, and αIL-4), or lineage-uncommitted cells (αIL-12p40). Supernatants were harvested every 24 h and analyzed by ELISA. (B) RNA was extracted at 96 h from LNC cultures as described in A for measurement of transcription factors by real-time RT-PCR. Levels were normalized to GAPDH. The data are shown as fold induction over the level in cells cultured under neutral conditions. (C) Purified T cells from IL-12– and IL-23–modulated cultures were transferred to naive syngeneic recipients (25 × 106 cells/mouse). Mice were killed at peak disease for histological analysis. The data shown are representative of four independent experiments. Asterisks indicate a significant difference when compared with the control group. *, P < 0.05 compared with recipients of lineage uncommitted T cells.