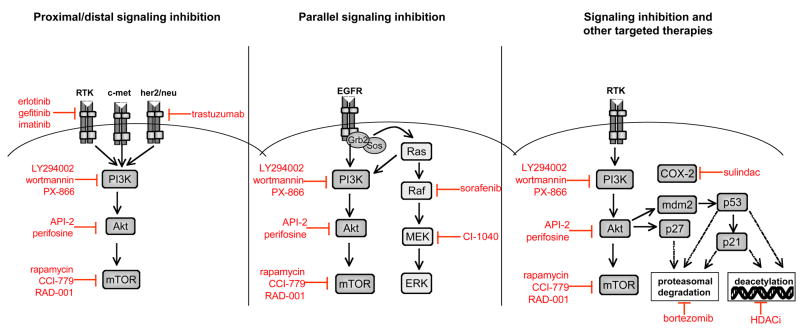
Figure 2. Combinatorial approaches with inhibitors of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.
Several approaches can be employed when combining pathway inhibitors with other targeted therapies. Inhibition of proximal pathway components, such as receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and oncogenes, combined with distal inhibition of Akt or mTOR may be an effective approach to circumvent feedback activation that could occur with distal inhibition alone (left panel). Alternatively, dual inhibition of parallel signaling pathways prevents compensatory activation of redundant pro-survival pathways (middle panel). Finally, pathway inhibition can be combined with several other types of targeted therapies, including inhibition of histone deacetylase complexes (HDAC), the proteasome and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) (right panel).