Fig. 2.
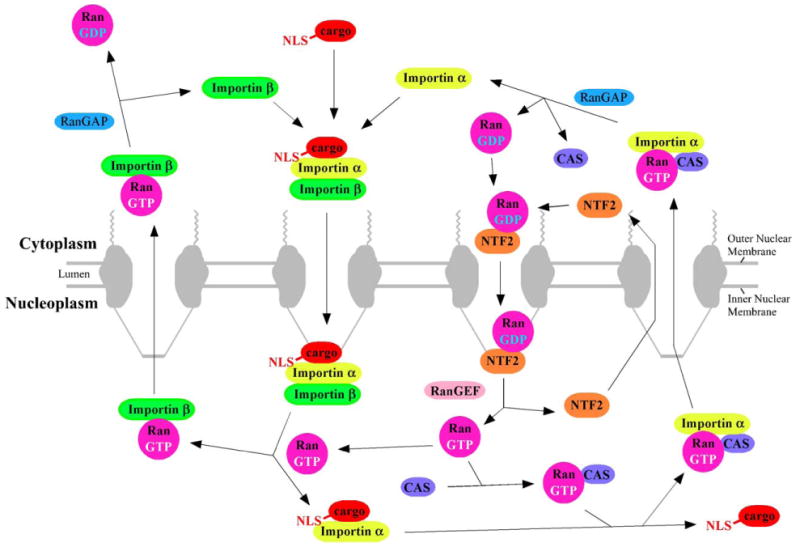
Transport pathways involved in NLS-mediated nuclear import. Nuclear localization sequences (NLSs) are typically recognized by a member of the importin-β family of import receptors. Sometimes an adaptor protein is required. In the case of the NLS of the SV40 large T antigen, this adaptor protein is importin-α [38]. The import complex (importin(s) plus cargo) is dissociated by Ran-GTP. Importins are recycled by export from the nucleus in a complex with Ran-GTP; as for import, sometimes an additional cofactor is required (e.g., CAS for importin-α). RanGAP activates the Ran GTPase, leading to GTP hydrolysis and dissociation of export cargo. Ran-GDP is recycled back to the nucleus with the assistance of NTF2. The chromosome-bound RanGEF catalyzes GDP/GTP exchange. See text for additional details.
