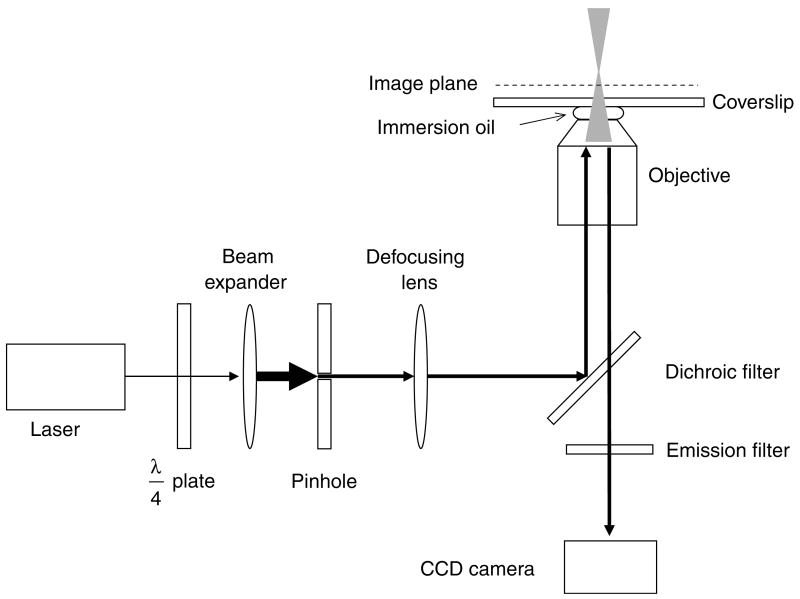
Fig. 3.
Narrow-field epifluorescence microscopy. This schematic shows the essential features of a narrow-field epifluorescence microscope setup that can be used for SMF. A quarter-wave (λ/4) plate is used to convert linearly polarized laser light to a circularly polarized beam, which is expanded to overfill the back aperture of the objective. A pinhole (typically 200–500 μm diameter) at a conjugate image plane confines the laser beam, reducing the illumination area within the image plane. The laser beam is converted to a diverging beam such that it focuses beyond the image plane.