Fig. 5.
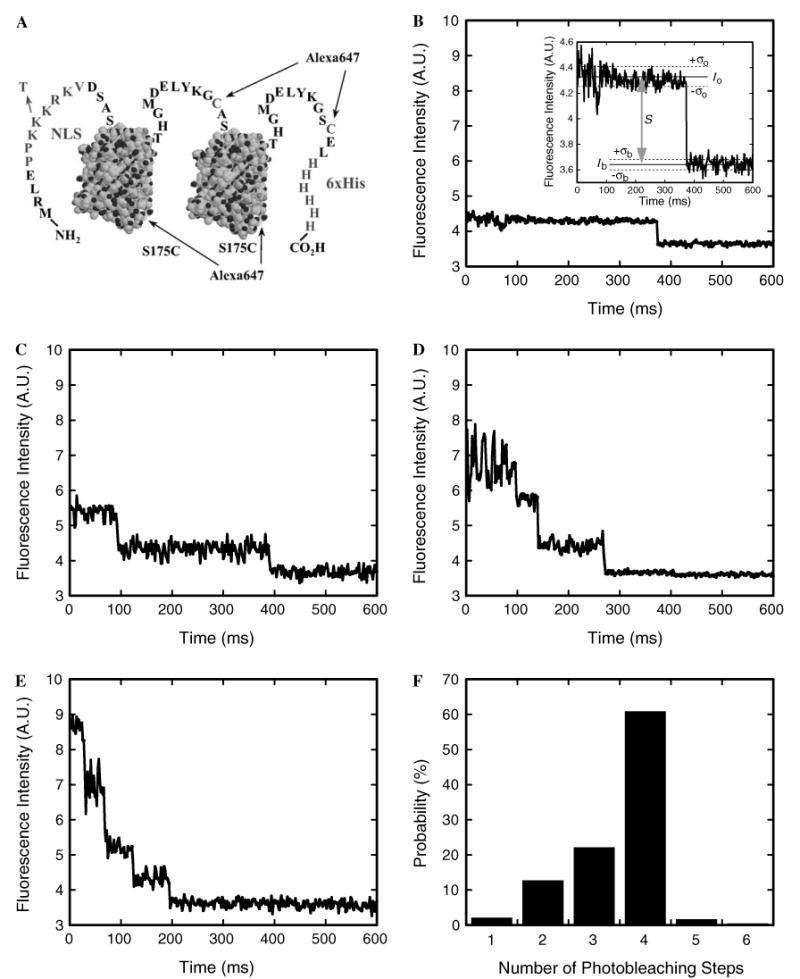
Photobleaching of NLS-2×GFP(4C) labeled with four Alexa647 molecules. (A) The NLS-2×GFP(4C) model cargo. Two identical GFP domains, represented here by structural models (PDB accession number 1C4F), have N- and C-terminal extensions and are linked by the peptide shown. The four identified cysteines (one in the linker, one in the C-terminal extension, and the S175C mutations in each of the two GFP domains) can each be labeled with a molecule of Alexa647 maleimide. The two wildtype cysteines in each GFP domain are unreactive toward maleimides. The N-terminal extension contains a nuclear localization sequence (NLS; PPKKKRKV) that targets the protein for importin-α/β-dependent transport. The indicated K → T mutation in the NLS blocks recognition by importin-α. The 6×His-tag assists with purification. (B–E) Photobleaching profile of an NLS-2×GFP(4C) cargo molecule labeled with (B) one, (C) two, (D) three, or (E) four Alexa647 molecules. Since each Alexa647 molecule exhibits quantized photobleaching, the number of dyes on the cargo can be determined by counting the number of photobleaching steps. The fluorescence intensity was integrated over a 6 × 6 pixel area. Inset in (B): expanded view of the photobleaching event. The signal intensity (S = Io − Ib) is estimated from the average intensities observed before (I0) and after (Ib) photobleaching. The standard deviation in the intensity while the dye is fluorescent (σo) is typically larger than the baseline noise (σb). The S/N is defined by Eq. (2). (F) Probability histogram for the number of photobleaching steps observed for individual cargo molecules. A sample from a preparation of NLS-2×GFP(4C) labeled with Alexa647 was immobilized on a coverslip surface, and the photobleaching profiles were determined as in B–E (N = 235). From these data, the average labeling ratio was calculated as 3.5 dye molecules per cargo molecule, in excellent agreement with the ratio (also 3.5) determined from absorption measurements of the labeled protein stock solution.
