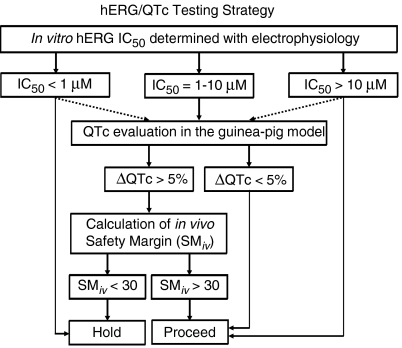
Figure 5.
A testing strategy incorporating the hERG (human ether a-go-go-related gene) electrophysiology and anaesthetized guinea-pig QTc (heart rate corrected QT interval of the ECG) assays. The solid lines represent the standard progression path, whereas the dashed lines represent exceptions on a case-by-case basis. Compounds are initially evaluated in a hERG electrophysiology assay conducted using the defined protocol described in Methods. Compounds with hERG IC50 values of >10 μM are usually progressed, whereas compounds with IC50 values of <1 μM are usually withheld. Compounds with hERG IC50 values between 1 and 10 μM are evaluated for their potential to prolong the QTc in a specific anaesthetized guinea-pig model (see Methods for protocol details). If a compound is found to prolong QTc in this model, an in vivo safety margin (SMiv) is calculated by dividing the peak drug concentration obtained from an anaesthetized guinea-pig study (where the QTc increased by more than 5%) by the peak drug concentration obtained during an efficacy study in an appropriate animal model. If the SMiv is greater than 30, the compound is further progressed; if the SMiv is less than 30, the compound is put on ‘hold', and research continues for an alternative clinical candidate.