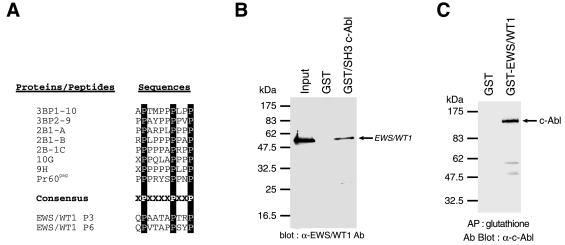
Figure 2.
EWS/WT1 and c-Abl can associate. (A) Alignment of consensus interacting motif for c-Abl SH3 domain among a series of downstream c-Abl targets, including two putative SH3 domain binding sites within EWS/WT1. The c-Abl SH3 consensus binding site of PxxxxPxxP has been reported (27, 31). (B) Association of EWS/WT1 with the SH3 domain of c-Abl. Bacterially produced (His)6-EWS/WT1 protein was incubated with either GST or GST-fusion c-Abl SH3 domain. An aliquot of the input (20%) and the pellets from GST pull-down assays were analyzed by 10% SDS/PAGE, and the bound EWS/WT1 proteins were detected with an anti-WT1 antibody (C-19; Santa Cruz) and chemiluminescence (DuPont/NEN). (C) Copurification of EWS/WT1 and c-Abl from cell extracts. Forty-eight hours after cotransfection of COS-7 cells with 10 μg of pcDNA3/Abl and either 10 μg of pcDNA3/GST or pcDNA3/GST-EWS/WT1, cell extracts were prepared as described in Materials and Methods and affinity-precipitated with glutathione beads. After fractionation on an 8% SDS/PAGE and transfer of the proteins to Immobilon PVDF membrane, the filter was preblocked in 5% nonfat skim milk in TBS-T (20 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 7.5/150 mM NaCl/0.1% Tween 20). A mAb against c-Abl [c-Abl(24–11); Santa Cruz Biotechnology] was used to interrogate the blot. Proteins were visualized with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody by using an ECL solution (DuPont/NEN) according to the manufacturer’s instruction.