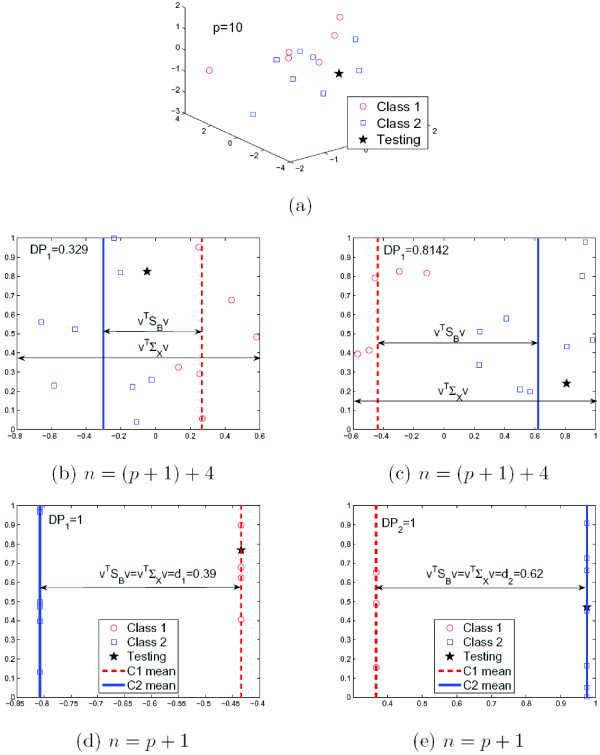
Figure 2.
(a) Shown here are the three dimensions with largest variance of the the randomly generated data in ℝ10. The horizontal axis in (b)-(e) corresponds to the direction v found by Fisher's LDA and when assuming the sample vector (star) corresponds to the first class in (b) and (d) and to the second class in (c) and (e). For visualization purposes, the samples have been randomly distributed about the vertical axis in (b)-(e). This helps illustrate the separability of the two classes shown as red (dashed) and blue (solid) lines. We now note that when n >p + 1, the value of DP is a good measure of separability. When n ≤ p + 1, DP collapses (Theorem 1), and di becomes the appropriate measure of discriminant ability.