Figure 3.
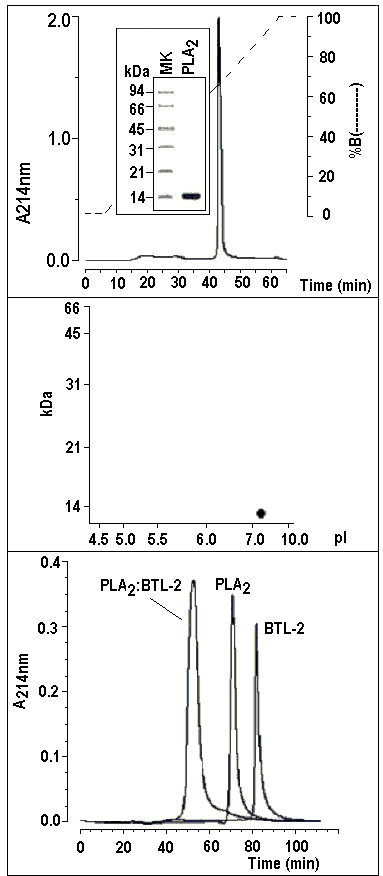
3a) The venom from the Crotalus durissus cascavella rattlesnake was fractionated by HPLC molecular exclusion chromatography (Superdex 75 column 1 × 60 Cmm) and the active fraction was subjected to Reverse Phase HPLC (μ-Bondapack C18 column) to obtain a high purity protein. 3b) Following the Laemmli method [43], a discontinuous electrophoresis was performed with a final acrylamide concentration of 12% in the running gel. All the samples and the molecular markers were treated with SDS and 1 M DTT and the run was conducted at 40 mA. The samples were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250. The SDS-PAGE profile of PLA2 showed high molecular homogeneity in a single band with an estimated molecular mass of approximately 14.0 kDa. 3c) Two dimensional electrophoresis showing one protein spot with molecular mass of around 14 kDa and pI of approximately 8.3. 3d) One milligram of sample was dissolved in 0.5 mL of 0.05 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.5, and applied to a Protein Pack TSK gel 3000 column (0.8 Cmm 30 Cmm) equilibrated with this same buffer. This procedure was performed with one milligram of each protein, incubated together and with all molecular mass markers to estimate the molecular weight of the samples. It is possible to observe a peak with an estimated molecular mass of 10 kDa from BTL-2, another with 15 kDa from PLA2 and another of approximately 24–26 kDa that corresponds to both incubated proteins.
