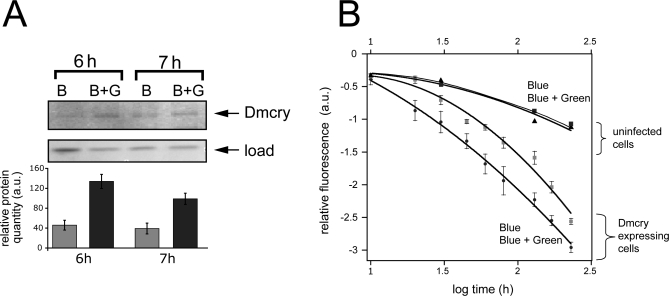
Figure 5. Green Light Alters Cryptochrome Photoconversion In Vivo That Correlates with Function.
(A) Living flies dark adapted for 3 d were irradiated with either blue (B) (445 ± 10 nm, 10 μmol m−2 s−1) light or bichromatically with (445 ± 10 nm, 10 μmol m−2 s−1) plus green (G) (550 ± 25 nm, 50 μmol m−2 s−1) light (B+G). Western blot with Dmcry antibody was as in Figure 2; equivalent load was verified both by Bradford assay and by staining of total proteins on gels. Three independent trials were performed with similar reduced response to B+G. a.u., arbitrary units.
(B) Dmcry photoreduction in living insect cell culture was monitored under conditions of bichromatic irradiation. Peak excitation efficiency at 450 nm was determined in duplicate samples over the indicated time course as above (Figure 1C and 1D). Samples were treated with either B at 25 μmol m−2 s−1 or bichromatically with B+G (550 ± 25 nm, 150 μmol m−2 s−1) light over the same interval. Deduced 450-nm peak intensities were plotted over time. No difference was observed in uninfected control cells under conditions of B or B+G irradiation.