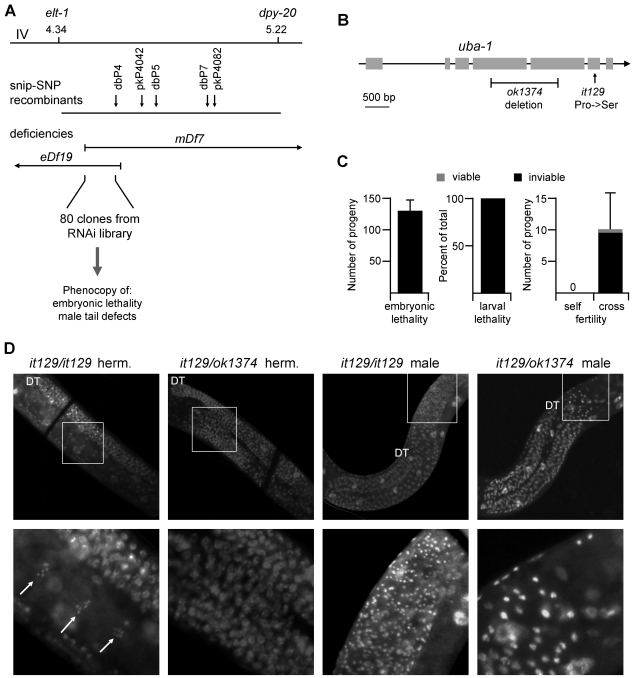
Figure 4. Cloning and complementation.
A) Schematic of cloning strategy. Shown at top is the interval of chromosome IV from elt-1 to dpy-20. Line two indicates the position of snip-SNPs identified in recombinant lines from N2 uba-1(it129) dpy-20(e1282) crossed with Hawaiian strain CB4856. The next two lines indicate the endpoints and overlapping regions of chromosomal deficiencies eDf19 and mDf7, which failed to complement uba-1(it129). Eighty genes within the 0.31 Mb overlap were screened by RNAi feeding for two uba-1(it129) phenotypes: embryonic lethality and male tail defects. B) Predicted gene structure of uba-1. Shown are position of the Pro1024Ser missense mutation identified in the it129 allele and extent of the deleted region of the ok1374 allele. C) Complementation data for it129/ok1374 heterozygotes. Assay conditions for F1 embryonic lethality (N = 6 hermaphrodites), larval lethality (minimum 500 embryos), and sperm-specific sterility (N = 10 hermaphrodites) were identical to those used to characterize it129 homozyogotes; see Figure 1 and accompanying text. D) Germ line defects in it129/ok1374 heterozyogotes. Germ line nuclei were visualized by DAPI staining of fixed adult animals. The distal tip (DT) of the gonad is indicated for orientation. Top row shows a single gonad arm from (left to right) an it129 homozygous hermaphrodite, it129/ok1374 heterozygous hermaphrodite, it129 homozygous male, and it129/ok1374 heterozygous male. Bottom row shows a high-magnification image of the boxed region of the proximal gonad. Arrows, oocyte nuclei in diakinesis.